Efficient in vivo bone formation by BMP-2 engineered human mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in a projection stereolithographically fabricated hydrogel scaffold
- PMID: 31412905
- PMCID: PMC6694509
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-019-1350-6
Efficient in vivo bone formation by BMP-2 engineered human mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in a projection stereolithographically fabricated hydrogel scaffold
Abstract
Background: Stem cell-based bone tissue engineering shows promise for bone repair but faces some challenges, such as insufficient osteogenesis and limited architecture flexibility of the cell-delivery scaffold.
Methods: In this study, we first used lentiviral constructs to transduce ex vivo human bone marrow-derived stem cells with human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) gene (BMP-hBMSCs). We then introduced these cells into a hydrogel scaffold using an advanced visible light-based projection stereolithography (VL-PSL) technology, which is compatible with concomitant cell encapsulation and amenable to computer-aided architectural design, to fabricate scaffolds fitting local physical and structural variations in different bones and defects.
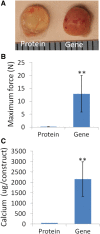
Results: The results showed that the BMP-hBMSCs encapsulated within the scaffolds had high viability with sustained BMP-2 gene expression and differentiated toward an osteogenic lineage without the supplement of additional BMP-2 protein. In vivo bone formation efficacy was further assessed using an intramuscular implantation model in severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) mice. Microcomputed tomography (micro-CT) imaging indicated rapid bone formation by the BMP-hBMSC-laden constructs as early as 14 days post-implantation. Histological examination revealed a mature trabecular bone structure with considerable vascularization. Through tracking of the implanted cells, we also found that BMP-hBMSC were directly involved in the new bone formation.
Conclusions: The robust, self-driven osteogenic capability and computer-designed architecture of the construct developed in this study should have potential applications for customized clinical repair of large bone defects or non-unions.
Keywords: 3D bioprinting; Bone formation; Bone tissue engineering; Ex vivo gene transduction; Gene therapy; Osteogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
[A novel tissue-engineered bone constructed by using human adipose-derived stem cells and biomimetic calcium phosphate scaffold coprecipitated with bone morphogenetic protein-2].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2017 Feb 18;49(1):6-15. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2017. PMID: 28202997 Chinese.
-
Delivery of VEGFA in bone marrow stromal cells seeded in copolymer scaffold enhances angiogenesis, but is inadequate for osteogenesis as compared with the dual delivery of VEGFA and BMP2 in a subcutaneous mouse model.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018 Jan 31;9(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13287-018-0778-4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29386057 Free PMC article.
-
VEGF and BMP-2 promote bone regeneration by facilitating bone marrow stem cell homing and differentiation.Eur Cell Mater. 2014 Jan 15;27:1-11; discussion 11-2. doi: 10.22203/ecm.v027a01. Eur Cell Mater. 2014. PMID: 24425156
-
Advanced Hydrogels as Exosome Delivery Systems for Osteogenic Differentiation of MSCs: Application in Bone Regeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 8;22(12):6203. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126203. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34201385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells modifications for enhanced bone targeting and bone regeneration.Regen Med. 2020 Apr;15(4):1579-1594. doi: 10.2217/rme-2019-0081. Epub 2020 Apr 16. Regen Med. 2020. PMID: 32297546 Review.
Cited by
-
mRNA encoding bone morphogenetic protein-2 facilitated peri-implant bone formation of titanium implants placed in rat femurs.Sci Rep. 2025 May 22;15(1):17852. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02931-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40404873 Free PMC article.
-
Programmable biomaterials for bone regeneration.Mater Today Bio. 2024 Oct 9;29:101296. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101296. eCollection 2024 Dec. Mater Today Bio. 2024. PMID: 39469314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancing Dentistry through Bioprinting: Personalization of Oral Tissues.J Funct Biomater. 2023 Oct 20;14(10):530. doi: 10.3390/jfb14100530. J Funct Biomater. 2023. PMID: 37888196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoclay Promotes Mouse Cranial Bone Regeneration Mainly through Modulating Drug Binding and Sustained Release.Appl Mater Today. 2020 Dec;21:100860. doi: 10.1016/j.apmt.2020.100860. Epub 2020 Oct 27. Appl Mater Today. 2020. PMID: 33225042 Free PMC article.
-
Neural Differentiation of Wisdom Tooth Follicle Stem Cells on a Nano-Hydrogel Scaffold Containing Salvia Chloroleucat to Treat Nerve injury in the Cancer of Nervous System.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023 Feb 1;24(2):649-658. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.2.649. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023. PMID: 36853316 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ewers R, Goriwoda W, Schopper C, Moser D, Spassova E. Histologic findings at augmented bone areas supplied with two different bone substitute materials combined with sinus floor lifting. Report of one case. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2004;15(1):96–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2004.00987.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

