Risk of Zika microcephaly correlates with features of maternal antibodies
- PMID: 31413072
- PMCID: PMC6781003
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20191061
Risk of Zika microcephaly correlates with features of maternal antibodies
Abstract
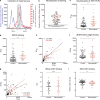
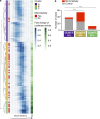
Zika virus (ZIKV) infection during pregnancy causes congenital abnormalities, including microcephaly. However, rates vary widely, and the contributing risk factors remain unclear. We examined the serum antibody response to ZIKV and other flaviviruses in Brazilian women giving birth during the 2015-2016 outbreak. Infected pregnancies with intermediate or higher ZIKV antibody enhancement titers were at increased risk to give birth to microcephalic infants compared with those with lower titers (P < 0.0001). Similarly, analysis of ZIKV-infected pregnant macaques revealed that fetal brain damage was more frequent in mothers with higher enhancement titers. Thus, features of the maternal antibodies are associated with and may contribute to the genesis of ZIKV-associated microcephaly.
© 2019 Robbiani et al.
Figures


References
-
- Adams Waldorf K.M., Stencel-Baerenwald J.E., Kapur R.P., Studholme C., Boldenow E., Vornhagen J., Baldessari A., Dighe M.K., Thiel J., Merillat S., et al. 2016. Fetal brain lesions after subcutaneous inoculation of Zika virus in a pregnant nonhuman primate. Nat. Med. 22:1256–1259. 10.1038/nm.4193 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adams Waldorf K.M., Nelson B.R., Stencel-Baerenwald J.E., Studholme C., Kapur R.P., Armistead B., Walker C.L., Merillat S., Vornhagen J., Tisoncik-Go J., et al. 2018. Congenital Zika virus infection as a silent pathology with loss of neurogenic output in the fetal brain. Nat. Med. 24:368–374. 10.1038/nm.4485 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- UM1 AI100663/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- D43 TW010540/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- P51 OD010425/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P51 OD011107/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI138938/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI133976/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI100989/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 TW009504/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI104002/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P51 OD011106/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- C06 RR015459/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- C06 RR020141/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P51 OD011092/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI037526/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD083091/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI083019/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI057229/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001866/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI124690/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R25 TW009338/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI129479/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI145296/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HD091032/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI121207/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U19 AI111825/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States

