A general approach for detecting expressed mutations in AML cells using single cell RNA-sequencing
- PMID: 31413257
- PMCID: PMC6694122
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-11591-1
A general approach for detecting expressed mutations in AML cells using single cell RNA-sequencing
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: A general approach for detecting expressed mutations in AML cells using single cell RNA-sequencing.Nat Commun. 2022 Jul 21;13(1):4216. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31995-w. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35864110 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
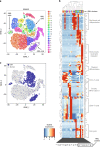
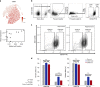
Virtually all tumors are genetically heterogeneous, containing mutationally-defined subclonal cell populations that often have distinct phenotypes. Single-cell RNA-sequencing has revealed that a variety of tumors are also transcriptionally heterogeneous, but the relationship between expression heterogeneity and subclonal architecture is unclear. Here, we address this question in the context of Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) by integrating whole genome sequencing with single-cell RNA-sequencing (using the 10x Genomics Chromium Single Cell 5' Gene Expression workflow). Applying this approach to five cryopreserved AML samples, we identify hundreds to thousands of cells containing tumor-specific mutations in each case, and use the results to distinguish AML cells (including normal-karyotype AML cells) from normal cells, identify expression signatures associated with subclonal mutations, and find cell surface markers that could be used to purify subclones for further study. This integrative approach for connecting genotype to phenotype is broadly applicable to any sample that is phenotypically and genetically heterogeneous.
Conflict of interest statement
S.W. and I.F. are employed by and hold shares in 10x Genomics. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

