Genetic induction and mechanochemical propagation of a morphogenetic wave
- PMID: 31413363
- PMCID: PMC8985608
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1492-9
Genetic induction and mechanochemical propagation of a morphogenetic wave
Abstract
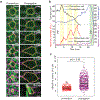
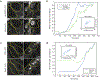
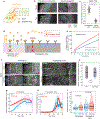
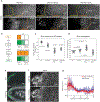
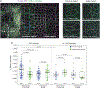
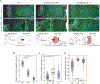
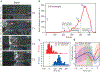
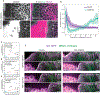
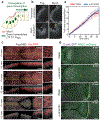
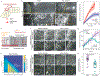
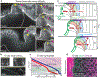
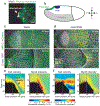
Tissue morphogenesis arises from coordinated changes in cell shape driven by actomyosin contractions. Patterns of gene expression regionalize cell behaviours by controlling actomyosin contractility. Here we report two modes of control over Rho1 and myosin II (MyoII) activation in the Drosophila endoderm. First, Rho1-MyoII are induced in a spatially restricted primordium via localized transcription of the G-protein-coupled receptor ligand Fog. Second, a tissue-scale wave of Rho1-MyoII activation and cell invagination progresses anteriorly away from the primordium. The wave does not require sustained gene transcription, and is not governed by regulated Fog delivery. Instead, MyoII inhibition blocks Rho1 activation and propagation, revealing a mechanical feedback driven by MyoII. We find that MyoII activation and invagination in each row of cells drives adhesion to the vitelline membrane mediated by integrins, apical spreading, MyoII activation and invagination in the next row. Endoderm morphogenesis thus emerges from local transcriptional initiation and a mechanically driven cycle of cell deformation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures





Comment in
-
Genetics and mechanics combine to guide the embryonic gut.Nature. 2019 Aug;572(7770):446-447. doi: 10.1038/d41586-019-02398-7. Nature. 2019. PMID: 31427801 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

