Torticaput versus Torticollis: Clinical Effects with Modified Classification and Muscle Selection
- PMID: 31413892
- PMCID: PMC6691609
- DOI: 10.7916/tohm.v0.647
Torticaput versus Torticollis: Clinical Effects with Modified Classification and Muscle Selection
Abstract
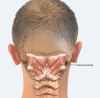
Background: Several different subtypes are distinguished in cervical dystonia, depending on their different levels of movement. In simple rotation, classified as torticollis spasmodicus, we now differentiate between torticollis and torticaput dependent on whether only the head or the neck is turned. The new classification system permits for different injection schemes.
Case reports: In a retrospective study of 22 patients, we examined whether modifying the injected muscles leads to improvement in the results as evaluated in the Toronto Western Spasmodic Torticollis Rating Scale (TWSTRS). The results showed that both injection schemes do in fact lead to improvements while differentiating between caput and collum has significantly better effects.
Discussion: Due to our results we recommend the classification differentiating between torticollis and torticaput type.
Keywords: Obliquus capitis inferior; TWSTRS; Torticaput; botulinum toxin; cervical dystonia; sonography; torticollis.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding: None. Conflicts of Interest: The authors report no conflict of interest. Ethics Statement: This study was performed in accordance with the ethical standards detailed in the Declaration of Helsinki. The authors’ institutional ethics committee has approved this study, and all patients have provided written informed consent.
Figures

References
-
- Reichel G. Cervical dystonia: a new phenomenological classification for botulinumtoxin therapy. Basal Ganglia 2011;1:5–12. doi: 10.1016/j.baga.2011.01.001 - DOI
-
- Consky ES, Basinki A, Belle L, Ranawaya R, Lang AE, et al. The Toronto Western Spasmodic Torticollis Rating Scale (TWSTRS): assessment of validity and inter-rater reliability. Neurology 1990;40(suppl 1):445.
-
- Tsui JK, Eisen A, Mak E, Carruthers J, Scott A, Calne DB. A pilot study on the use of botulinum toxin in spasmodic torticollis. Can J Neurol Sci 1985;12:314–316. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

