Targeting the C-terminus of galectin-9 induces mesothelioma apoptosis and M2 macrophage depletion
- PMID: 31413910
- PMCID: PMC6682368
- DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2019.1601482
Targeting the C-terminus of galectin-9 induces mesothelioma apoptosis and M2 macrophage depletion
Abstract
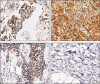
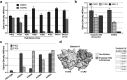
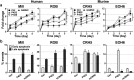
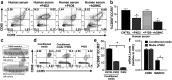
Galectin-9 has emerged as a promising biological target for cancer immunotherapy due to its role as a regulator of macrophage and T-cell differentiation. In addition, its expression in tumor cells modulates tumor cell adhesion, metastasis, and apoptosis. Malignant mesothelioma (MM) is an aggressive neoplasm of the mesothelial cells lining the pleural and peritoneal cavities, and in this study, we found that both human MM tissues and mouse MM cells express high levels of galectin-9. Using a novel monoclonal antibody (mAb) (Clone P4D2) that binds the C-terminal carbohydrate recognition domain (CRD) of galectin-9, we demonstrate unique agonistic properties resulting in MM cell apoptosis. Furthermore, the P4D2 mAb reduced tumor-associated macrophages differentiation toward a protumor phenotype. Importantly, these effects exerted by the P4D2 mAb were observed in both human and mouse in vitro experiments and not observed with another antigalectin-9 specific mAb (clone P1D9) that engages the N-terminus CRD of galectin-9. In syngeneic murine models of MM, P4D2 mAb treatment inhibited tumor growth and improved survival, with tumors from P4D2-treated mice exhibited reduced infiltration of tumor-associated M2 macrophages. This was consistent with an increased production of inducible nitric oxide synthase, which is a major enzyme-regulating macrophage inflammatory response to cancer. These data suggest that using an antigalectin 9 mAb with agonistic properties similar to those exerted by galectin-9 may provide a novel multitargeted strategy for the treatment of mesothelioma and possibly other galectin-9 expressing tumors.
Keywords: Lectins; agonist monoclonal antibody; galectin 9; immunotherapy; macrophages; mesothelioma.
Figures


References
-
- Tureci O, Schmitt H, Fadle N, Pfreundschuh M, Sahin U.. Molecular definition of a novel human galectin which is immunogenic in patients with Hodgkin‘s disease. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:6416–6422. - PubMed
-
- Wada J, Kanwar YS.. Identification and characterization of galectin-9, a novel beta-galactoside-binding mammalian lectin. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:6078–6086. - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Feng J, Geng S, Geng S, Wei H, Chen G, Li X, Wang L, Wang R, Peng H, et al. The N- and C-terminal carbohydrate recognition domains of galectin-9 contribute differently to its multiple functions in innate immunity and adaptive immunity. Mol Immunol. 2011;48:670–677. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2010.11.011. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kuroda J, Yamamoto M, Nagoshi H, Kobayashi T, Sasaki N, Shimura Y, Horiike S, Kimura S, Yamauchi A, Hirashima M, et al. Targeting activating transcription factor 3 by galectin-9 induces apoptosis and overcomes various types of treatment resistance in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Mol Cancer Res. 2010;8:994–1001. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-10-0040. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
