Computed tomography pulmonary angiograms using a novel dual-layer spectral detector: Adjusted window settings are essential for diagnostic image quality
- PMID: 31415352
- PMCID: PMC6831234
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016606
Computed tomography pulmonary angiograms using a novel dual-layer spectral detector: Adjusted window settings are essential for diagnostic image quality
Abstract
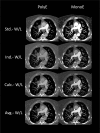
Objective: The aim of this study was to determine optimal window settings for conventional polyenergetic and virtual monoenergetic images derived from computed tomography pulmonary angiogram (CTPA) examinations of a novel dual-layer spectral detector computed tomography system (DLCT).
Methods: Monoenergetic (40 keV) and polyenergetic images of 50 CTPA examinations were calculated and the best individual window width and level (W/L) values were manually assessed. Optimized values were obtained afterwards based on regression analysis. Diameters of standardized pulmonary artery segments and subjective image quality parameters were evaluated and compared.
Results: Attenuation and contrast-to-noise values were higher in monoenergetic than in polyenergetic images (P≤.001). Averaged best individual W/L for polyenergetic and monoenergetic were 1020/170 and 2070/480 HU, respectively.All adjusted W/L-settings varied significantly compared to standard settings (700/100 HU) and obtained higher subjective image quality scores. A systematic overestimation of artery diameters for standard window settings in monoenergetic images was observed.
Conclusions: Appropriate W/L-settings are required to assess polyenergetic and monoenergetic CTPA images of a novel DLCT. W/L-settings of 1020/170 HU and 2070/480 HU were found to be the best averaged values for polyenergetic and monoenergetic CTPA images, respectively.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Optimisation of window settings for traditional and noise-optimised virtual monoenergetic imaging in dual-energy computed tomography pulmonary angiography.Eur Radiol. 2018 Apr;28(4):1393-1401. doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-5059-6. Epub 2017 Oct 10. Eur Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29018926
-
Poly-energetic and virtual mono-energetic images from a novel dual-layer spectral detector CT: optimization of window settings is crucial to improve subjective image quality in abdominal CT angiographies.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2018 Mar;43(3):742-750. doi: 10.1007/s00261-017-1241-1. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2018. PMID: 28677003
-
Evaluation of Virtual Monoenergetic Images on Pulmonary Vasculature Using the Dual-Layer Detector-Based Spectral Computed Tomography.J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2018 Nov/Dec;42(6):858-865. doi: 10.1097/RCT.0000000000000748. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2018. PMID: 29659426
-
Comparison of virtual monoenergetic and polyenergetic images reconstructed from dual-layer detector CT angiography of the head and neck.Eur Radiol. 2018 Mar;28(3):1102-1110. doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-5081-8. Epub 2017 Oct 10. Eur Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29018958
-
Carotid and cerebrovascular dual-energy computed tomography angiography: Optimization of window settings for virtual monoenergetic imaging reconstruction.Eur J Radiol. 2020 Sep;130:109166. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.109166. Epub 2020 Jul 9. Eur J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32693314
Cited by
-
Generally applicable window settings of low-keV virtual monoenergetic reconstructions in dual-layer CT-angiography of the head and neck.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2021 Aug;11(8):3408-3417. doi: 10.21037/qims-20-1140. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2021. PMID: 34341719 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albrecht MH, Trommer J, Wichmann JL, et al. Comprehensive comparison of virtual monoenergetic and linearly blended reconstruction techniques in third-generation dual-source dual-energy computed tomography angiography of the thorax and abdomen. Invest Radiol 2016;51:582–90. - PubMed
-
- Gupta S, Wagner-Bartak N, Jensen CT, et al. Dual-energy CT of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: reproducibility of primary tumor measurements and assessment of tumor conspicuity and margin sharpness. Abdom Radiol 2016;41:1317–24. - PubMed
-
- Weiss J, Notohamiprodjo M, Bongers M, et al. Effect of noise-optimized monoenergetic postprocessing on diagnostic accuracy for detecting incidental pulmonary embolism in portal-venous phase dual-energy computed tomography. Invest Radiol 2017;52:142–7. - PubMed
-
- Lago KN, Vallejos J, Capuñay C, et al. Dual-energy computed tomography for the detection of focal liver lesions. Radiologia 2017;59:306–12. - PubMed
-
- Neuhaus V, Abdullayev N, Große Hokamp N, et al. Improvement of image quality in unenhanced dual-layer CT of the head using virtual monoenergetic images compared with polyenergetic single-energy CT. Invest Radiol 2017;52:470–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

