Computed tomography pulmonary angiograms using a novel dual-layer spectral detector: Adjusted window settings are essential for diagnostic image quality
- PMID: 31415352
- PMCID: PMC6831234
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016606
Computed tomography pulmonary angiograms using a novel dual-layer spectral detector: Adjusted window settings are essential for diagnostic image quality
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to determine optimal window settings for conventional polyenergetic and virtual monoenergetic images derived from computed tomography pulmonary angiogram (CTPA) examinations of a novel dual-layer spectral detector computed tomography system (DLCT).
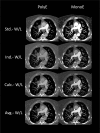
Methods: Monoenergetic (40 keV) and polyenergetic images of 50 CTPA examinations were calculated and the best individual window width and level (W/L) values were manually assessed. Optimized values were obtained afterwards based on regression analysis. Diameters of standardized pulmonary artery segments and subjective image quality parameters were evaluated and compared.
Results: Attenuation and contrast-to-noise values were higher in monoenergetic than in polyenergetic images (P≤.001). Averaged best individual W/L for polyenergetic and monoenergetic were 1020/170 and 2070/480 HU, respectively.All adjusted W/L-settings varied significantly compared to standard settings (700/100 HU) and obtained higher subjective image quality scores. A systematic overestimation of artery diameters for standard window settings in monoenergetic images was observed.
Conclusions: Appropriate W/L-settings are required to assess polyenergetic and monoenergetic CTPA images of a novel DLCT. W/L-settings of 1020/170 HU and 2070/480 HU were found to be the best averaged values for polyenergetic and monoenergetic CTPA images, respectively.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Albrecht MH, Trommer J, Wichmann JL, et al. Comprehensive comparison of virtual monoenergetic and linearly blended reconstruction techniques in third-generation dual-source dual-energy computed tomography angiography of the thorax and abdomen. Invest Radiol 2016;51:582–90. - PubMed
-
- Gupta S, Wagner-Bartak N, Jensen CT, et al. Dual-energy CT of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: reproducibility of primary tumor measurements and assessment of tumor conspicuity and margin sharpness. Abdom Radiol 2016;41:1317–24. - PubMed
-
- Weiss J, Notohamiprodjo M, Bongers M, et al. Effect of noise-optimized monoenergetic postprocessing on diagnostic accuracy for detecting incidental pulmonary embolism in portal-venous phase dual-energy computed tomography. Invest Radiol 2017;52:142–7. - PubMed
-
- Lago KN, Vallejos J, Capuñay C, et al. Dual-energy computed tomography for the detection of focal liver lesions. Radiologia 2017;59:306–12. - PubMed
-
- Neuhaus V, Abdullayev N, Große Hokamp N, et al. Improvement of image quality in unenhanced dual-layer CT of the head using virtual monoenergetic images compared with polyenergetic single-energy CT. Invest Radiol 2017;52:470–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

