Proteasome serves as pivotal regulator in Angiostrongylus cantonensis-induced eosinophilic meningoencephalitis
- PMID: 31415587
- PMCID: PMC6695157
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220503
Proteasome serves as pivotal regulator in Angiostrongylus cantonensis-induced eosinophilic meningoencephalitis
Abstract
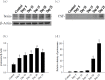
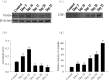
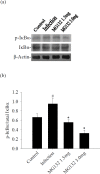
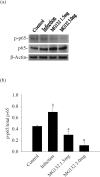
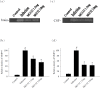
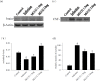
Proteasome primarily degrades the unneeded or damaged proteins by proteolysis. Disruption of the brain barrier and its resulting meningoencephalitis caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis are important pathological events in non-permissive hosts. In this study, the results showed upregulated proteasome during A. cantonensis infection. Occludin degradation and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) activity were significantly increased in infected mice than in uninfected mice. Moreover, confocal immunoflourescence microscopy showed that occludin was co-localized with MMP-9. The infected-mice were treated with proteasomal activity inhibitor MG132 by 1.5 and 3.0 mg/kg/day, which resulted in significantly reduced protein levels of phosphorylated IκBα (P<0.05) compared with the untreated control. The phosphorylated nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) showed similar result. In addition, MMP-9 activity and occludin degradation were reduced because of MG132 treatment. These results suggested that the proteasome in A. cantonensis infection degraded phosphorylated IκBα, modulated phosphorylated NF-κB, and then regulated the activation of MMP-9 and occludin degradation. Proteasome alterations were presented in eosinophilic meningitis of BALB/c mice and may contribute to the pathophysiology of eosinophilic meningitis by increasing occludin degradation. This molecule would serve as pivotal regulator in A. cantonensis-induced eosinophilic meningoencephalitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 leads to claudin-5 degradation via the NF-κB pathway in BALB/c mice with eosinophilic meningoencephalitis caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e53370. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053370. Epub 2013 Mar 7. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23505411 Free PMC article.
-
Development of brain injury in mice by Angiostrongylus cantonensis infection is associated with the induction of transcription factor NF-kappaB, nuclear protooncogenes, and protein tyrosine phosphorylation.Exp Parasitol. 2000 Jul;95(3):202-8. doi: 10.1006/expr.2000.4530. Exp Parasitol. 2000. PMID: 10964648
-
Peroxisome-Proliferator Activator Receptor γ in Mouse Model with Meningoencephalitis Caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis.J Parasitol. 2021 Mar 1;107(2):205-213. doi: 10.1645/19-182. J Parasitol. 2021. PMID: 33684197
-
[Advances in pathogenic mechanisms of Angiostrongylus cantonensis infection].Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2019 Mar 16;31(1):98-104. doi: 10.16250/j.32.1374.2018305. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31016931 Review. Chinese.
-
Angiostrongyliasis cantonensis (eosinophilic meningitis, Alicata's disease).Contemp Neurol Ser. 1975;12:133-64. Contemp Neurol Ser. 1975. PMID: 1095293 Review.
Cited by
-
Angiostrongylus cantonensis infection induces MMP-9 and causes tight junction protein disruption associated with Purkinje cell degeneration.Parasitol Res. 2020 Oct;119(10):3433-3441. doi: 10.1007/s00436-020-06840-y. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Parasitol Res. 2020. PMID: 32789733
-
Activation of the COX-2/mPGES-1/PGE-2 cascade through the NLRP3 inflammasome contributes to Angiostrongylus cantonensis-induced eosinophilic meningoencephalitis.Parasitol Res. 2025 Jan 20;124(1):9. doi: 10.1007/s00436-025-08454-8. Parasitol Res. 2025. PMID: 39832004 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hsu WY, Chen JY, Chien CT, Chi CS, Han NT. Eosinophilic meningitis caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Pediatr Infect Dis J 1990; 9: 443–445. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

