Plant-Microbe Interactions Facing Environmental Challenge
- PMID: 31415751
- PMCID: PMC6697056
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2019.07.009
Plant-Microbe Interactions Facing Environmental Challenge
Abstract
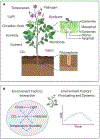
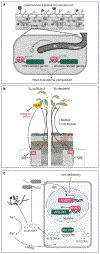
In the past four decades, tremendous progress has been made in understanding how plants respond to microbial colonization and how microbial pathogens and symbionts reprogram plant cellular processes. In contrast, our knowledge of how environmental conditions impact plant-microbe interactions is less understood at the mechanistic level, as most molecular studies are performed under simple and static laboratory conditions. In this review, we highlight research that begins to shed light on the mechanisms by which environmental conditions influence diverse plant-pathogen, plant-symbiont, and plant-microbiota interactions. There is a great need to increase efforts in this important area of research in order to reach a systems-level understanding of plant-microbe interactions that are more reflective of what occurs in nature.
Keywords: abiotic stress; circadian clock; climate change; humidity; innate immunity; light; nutrient; plant pathogen; symbiosis; temperature.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Alcazar R, and Parker JE (2011). The impact of temperature on balancing immune responsiveness and growth in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 16, 666–675. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

