Ega3 from the fungal pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus is an endo-α-1,4-galactosaminidase that disrupts microbial biofilms
- PMID: 31416836
- PMCID: PMC6746457
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009910
Ega3 from the fungal pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus is an endo-α-1,4-galactosaminidase that disrupts microbial biofilms
Abstract
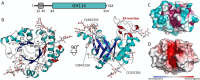
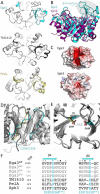
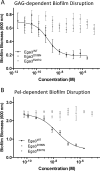
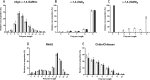
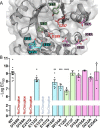
Aspergillus fumigatus is an opportunistic fungal pathogen that causes both chronic and acute invasive infections. Galactosaminogalactan (GAG) is an integral component of the A. fumigatus biofilm matrix and a key virulence factor. GAG is a heterogeneous linear α-1,4-linked exopolysaccharide of galactose and GalNAc that is partially deacetylated after secretion. A cluster of five co-expressed genes has been linked to GAG biosynthesis and modification. One gene in this cluster, ega3, is annotated as encoding a putative α-1,4-galactosaminidase belonging to glycoside hydrolase family 114 (GH114). Herein, we show that recombinant Ega3 is an active glycoside hydrolase that disrupts GAG-dependent A. fumigatus and Pel polysaccharide-dependent Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms at nanomolar concentrations. Using MS and functional assays, we demonstrate that Ega3 is an endo-acting α-1,4-galactosaminidase whose activity depends on the conserved acidic residues, Asp-189 and Glu-247. X-ray crystallographic structural analysis of the apo Ega3 and an Ega3-galactosamine complex, at 1.76 and 2.09 Å resolutions, revealed a modified (β/α)8-fold with a deep electronegative cleft, which upon ligand binding is capped to form a tunnel. Our structural analysis coupled with in silico docking studies also uncovered the molecular determinants for galactosamine specificity and substrate binding at the -2 to +1 binding subsites. The findings in this study increase the structural and mechanistic understanding of the GH114 family, which has >600 members encoded by plant and opportunistic human pathogens, as well as in industrially used bacteria and fungi.
Keywords: Aspergillus; biofilm; carbohydrate biosynthesis; carbohydrate processing; enzyme mechanism; exopolysaccharide matrix; galactosaminogalactan (GAG); glycoside hydrolase; glycoside hydrolase 114 (GH114); protein structure; virulence factor.
© 2019 Bamford et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures


References
-
- Stevens D. A., Moss R. B., Kurup V. P., Knutsen A. P., Greenberger P., Judson M. A., Denning D. W., Crameri R., Brody A. S., Light M., Skov M., Maish W., Mastella G., Participants in the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Consensus Conference (2003) Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in cystic fibrosis–state of the art: Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Consensus Conference. Clin. Infect. Dis. 37, Suppl., 3, S225–S264 10.1086/376525 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Knutsen A. P., and Slavin R. G. (1990) Cystic Fibrosis (Richard B.S., ed) Vol 1, pp. 103–118, Humana Press, Totowa, NJ: 10.1007/978-1-4612-0475-6_7 - DOI
-
- Gresnigt M. S., Bozza S., Becker K. L., Joosten L. A., Abdollahi-Roodsaz S., van der Berg W. B., Dinarello C. A., Netea M. G., Fontaine T., De Luca A., Moretti S., Romani L., Latge J. P., and van de Veerdonk F. L. (2014) A polysaccharide virulence factor from Aspergillus fumigatus elicits anti-inflammatory effects through induction of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. PLoS Pathog. 10, e1003936 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003936 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

