The CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Protein Family: Its Roles in MDSC Expansion and Function
- PMID: 31417568
- PMCID: PMC6684943
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01804
The CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Protein Family: Its Roles in MDSC Expansion and Function
Abstract
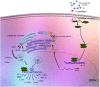
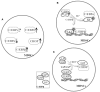
Immunosuppressive cells have been highlighted in research due to their roles in tumor progression and treatment failure. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) are among the major immunosuppressive cell populations in the tumor microenvironment, and transcription factors (TFs) are likely involved in MDSC expansion and activation. As key regulatory TFs, members of the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) family possibly modulate many biological processes, including cell growth, differentiation, metabolism, and death. Current evidence suggests that C/EBPs maintain critical regulation of MDSCs and are involved in the differentiation and function of MDSCs within the tumor microenvironment. To better understand the MDSC-associated transcriptional network and identify new therapy targets, we herein review recent findings about the C/EBP family regarding their participation in the expansion and function of MDSCs.
Keywords: C/EBPs; differentiation; immunosuppression; myeloid-derived suppressor cells; transcription factors.
Figures
References
-
- Tian X, Ma J, Wang T, Tian J, Zhang Y, Mao L, et al. Long non-coding RNA HOXA transcript antisense RNA myeloid-specific 1-HOXA1 axis downregulates the immunosuppression activity of granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells in lung cancer. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:473 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00473 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

