Waterlogging Tolerance at Germination in Field Pea: Variability, Genetic Control, and Indirect Selection
- PMID: 31417583
- PMCID: PMC6682692
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00953
Waterlogging Tolerance at Germination in Field Pea: Variability, Genetic Control, and Indirect Selection
Abstract
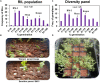
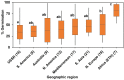
In the Eastern Gangetic Plain of South Asia field pea (Pisum sativum L.) is often grown as a relay crop where soil waterlogging (WL) causes germination failure. To assess if selection for WL tolerance is feasible, we studied the response to WL stress at germination stage in a recombinant inbred line (RIL) population from a bi-parental cross between WL-contrasting parents and in a diversity panel to identify extreme phenotypes, understand the genetics of WL tolerance and find traits for possible use in indirect selection. The RIL population and the diversity panel were screened to test the ability of germination under both waterlogged and drained soils. A total of 50, most WL tolerant and sensitive, genotypes from each of both the RIL and the diversity panel were further evaluated to assay testa integrity/leakage in CaSO4 solution. Morphological characterization of both populations was undertaken. A wide range of variation in the ability to germination in waterlogged soil was observed in the RIL population (6-93%) and the diversity panel (5-100%) with a high broad-sense heritability (H 2 > 85%). The variation was continuously distributed indicating polygenic control. Most genotypes with a dark colored testa (90%) were WL tolerant, whereas those with a light colored testa were all WL sensitive in both the RIL population and diversity panel. Testa integrity, measured by electrical conductivity of the leakage solute, was strongly associated with WL tolerance in the RIL population (r G = -1.00) and the diversity panel (r G = -0.90). Therefore, testa integrity can be effectively used in indirect selection for WL tolerance. Response to selection for WL tolerance at germination is confidently predicted enabling the adaptation of the ancient model pea to extreme precipitation events at germination.
Keywords: Pisum sp.; germination; indirect selection; secondary traits; waterlogging tolerance.
Figures


References
-
- Ali M. O., Sarker A. (2013). More benefit from less land: a new rice-pea-rice cropping pattern for resource-poor farmers of Bangladesh. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. B 3 204–210.
-
- Arcan I., Yemenicioğlu A. (2009). Antioxidant activity and phenolic content of fresh and dry nuts with or without the seed coat. J. Food Compost. Anal. 22 184–188. 10.1016/j.jfca.2008.10.016 - DOI
-
- Armstrong W., Drew M. C. (2002). “Root growth and metabolism under oxygen deficiency,” in Plant Roots: The Hidden Half, eds Waisel Y., Eshel A., Kafkafi U. (New York, NY: CRC Press; ), 729–761. 10.1201/9780203909423.ch42 - DOI
-
- Cooper M., Delacy I. H., Basford K. E. (1996). “Relationships among analytical methods used to analyse genotypic adaptation in multi-environment trials,” in Plant Adaptation and Crop Improvement, eds Cooper M., Hammer G. L. (Oxon: CAB International; ), 193–224.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

