Disease severity and minimal clinically important differences in clinical outcome assessments for Alzheimer's disease clinical trials
- PMID: 31417957
- PMCID: PMC6690415
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trci.2019.06.005
Disease severity and minimal clinically important differences in clinical outcome assessments for Alzheimer's disease clinical trials
Abstract
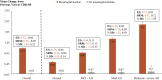
Introduction: This study estimated the minimal clinically important difference (MCID) for Mini Mental State Examination, Clinical Dementia Rating Scale sum of boxes, and Functional Activities Questionnaire across the Alzheimer's disease (AD) spectrum.
Methods: Retrospective analysis of the National Alzheimer's Coordinating Center Uniform Data Set (9/2005-9/2016) and MCID for clinical outcomes were estimated using anchor-based (clinician's assessment of meaningful decline) and distribution-based (1/2 baseline standard deviation) approaches, stratified by severity of cognitive impairment.
Results: On average, a 1-3 point decrease in Mini Mental State Examination, 1-2 point increase in Clinical Dementia Scale sum of boxes, and 3-5 point increase in Functional Activities Questionnaire were indicative of a meaningful decline. The MCID values generally increased by disease severity; the effect size and standardized response mean for those with meaningful decline were consistently in the acceptable ranges for MCID.
Discussion: These findings can inform design and interpretation of future clinical trials.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; CDR; FAQ; MCID; MMSE; Meaningful decline.
Figures
References
-
- Molnar F.J., Man-Son-Hing M., Fergusson D. Systematic review of measures of clinical significance employed in randomized clinical trials for drugs for dementia. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2009;57:536–546. - PubMed
-
- King M.T. A point of minimal important difference (MID): a critique of terminology and methods. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2011;11:171–184. - PubMed
-
- Jaeschke R., Singer J., Guyatt G.H. Measurement of health status: ascertaining the minimal clinically important difference. Controlled Clin Trials. 1989;10:407–415. - PubMed
-
- Green Park Collaborative, Evidence guidance document: design of clinical studies of pharmacologic therapies for Alzheimer's disease, Center for Medical Technology Policy. 2013. Available at: http://www.cmtpnet.org/docs/resources/GPC_Evidence_Guidance_Document_-_A.... Accessed September 10, 2018.
-
- Webster L., Groskreutz D., Grinbergs-Saull A., Howard R., O'Brien J.T., Mountain G. Core outcome measures for interventions to prevent or slow the progress of dementia for people living with mild to moderate dementia: systematic review and consensus recommendations. 2017. https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0179521 2017. Available at: - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- P50 AG005142/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016573/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG047266/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG025688/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005138/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG047366/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG019610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG028383/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG033514/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013854/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG053760/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010124/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG023501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005131/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG035982/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG008702/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG016976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG008051/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013846/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG047270/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005136/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG049638/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG012300/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005134/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG008017/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062715/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
