Long-read amplicon denoising
- PMID: 31418021
- PMCID: PMC6765106
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkz657
Long-read amplicon denoising
Abstract
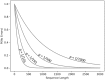
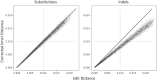
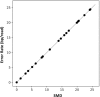
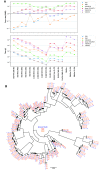
Long-read next-generation amplicon sequencing shows promise for studying complete genes or genomes from complex and diverse populations. Current long-read sequencing technologies have challenging error profiles, hindering data processing and incorporation into downstream analyses. Here we consider the problem of how to reconstruct, free of sequencing error, the true sequence variants and their associated frequencies from PacBio reads. Called 'amplicon denoising', this problem has been extensively studied for short-read sequencing technologies, but current solutions do not always successfully generalize to long reads with high indel error rates. We introduce two methods: one that runs nearly instantly and is very accurate for medium length reads and high template coverage, and another, slower method that is more robust when reads are very long or coverage is lower. On two Mock Virus Community datasets with ground truth, each sequenced on a different PacBio instrument, and on a number of simulated datasets, we compare our two approaches to each other and to existing algorithms. We outperform all tested methods in accuracy, with competitive run times even for our slower method, successfully discriminating templates that differ by a just single nucleotide. Julia implementations of Fast Amplicon Denoising (FAD) and Robust Amplicon Denoising (RAD), and a webserver interface, are freely available.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IPED: a highly efficient denoising tool for Illumina MiSeq Paired-end 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2016 Apr 29;17(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s12859-016-1061-2. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27130479 Free PMC article.
-
Improving the sensitivity of long read overlap detection using grouped short k-mer matches.BMC Genomics. 2019 Apr 4;20(Suppl 2):190. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5475-x. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30967123 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing using two next-generation sequencing technologies for phylogenetic analysis of the rumen bacterial community in steers.J Microbiol Methods. 2016 Aug;127:132-140. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2016.06.004. Epub 2016 Jun 6. J Microbiol Methods. 2016. PMID: 27282101
-
A hybrid and scalable error correction algorithm for indel and substitution errors of long reads.BMC Genomics. 2019 Dec 20;20(Suppl 11):948. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6286-9. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31856721 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive evaluation of long read error correction methods.BMC Genomics. 2020 Dec 21;21(Suppl 6):889. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-07227-0. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 33349243 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ultra-accurate microbial amplicon sequencing with synthetic long reads.Microbiome. 2021 Jun 5;9(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s40168-021-01072-3. Microbiome. 2021. PMID: 34090540 Free PMC article.
-
FEZF2 and AIRE1: An Evolutionary Trade-off in the Elimination of Auto-reactive T Cells in the Thymus.J Mol Evol. 2024 Feb;92(1):72-86. doi: 10.1007/s00239-024-10157-0. Epub 2024 Jan 29. J Mol Evol. 2024. PMID: 38285197
-
Multivariate mining of an alpaca immune repertoire identifies potent cross-neutralizing SARS-CoV-2 nanobodies.Sci Adv. 2022 Mar 25;8(12):eabm0220. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abm0220. Epub 2022 Mar 25. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35333580 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomics and full-length Tprk profiling of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum reinfection.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020 Apr 6;14(4):e0007921. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007921. eCollection 2020 Apr. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 32251462 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Multiplexed Phage Display, High-Throughput Sequencing, and Functional Assays as a Platform for Identifying Modulatory VHHs Targeting the FSHR.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 4;24(21):15961. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115961. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958944 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rogers M.B., Song T., Sebra R., Greenbaum B.D., Hamelin M.-E., Fitch A., Twaddle A., Cui L., Holmes E.C., Boivin G. et al. .. Intrahost dynamics of antiviral resistance in influenza A virus reflect complex patterns of segment linkage, reassortment, and natural selection. MBio. 2015; 6:e02464-14. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Landais E., Murrell B., Briney B., Murrell S., Rantalainen K., Berndsen Z.T., Ramos A., Wickramasinghe L., Smith M.L., Eren K. et al. .. HIV envelope glycoform heterogeneity and localized diversity govern the initiation and maturation of a V2 apex broadly neutralizing antibody lineage. Immunity. 2017; 47:990–1003. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

