Measuring extracellular volume fraction by MRI: First verification of values given by clinical sequences
- PMID: 31418490
- PMCID: PMC6900009
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.27938
Measuring extracellular volume fraction by MRI: First verification of values given by clinical sequences
Abstract
Purpose: To verify MR measurements of myocardial extracellular volume fraction (ECV) based on clinically applicable T1-mapping sequences against ECV measurements by radioisotope tracer in pigs and to relate the results to those obtained in volunteers.
Methods: Between May 2016 and March 2017, 8 volunteers (25 ± 4 years, 3 female) and 8 pigs (4 female) underwent ECV assessment with SASHA, MOLLI5(3b)3, MOLLI5(3s)3, and MOLLI5s(3s)3s. Myocardial ECV was measured independently in pigs using a radioisotope tracer method.
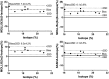
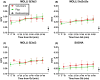
Results: In pigs, ECV in normal myocardium was not different between radioisotope (average ± standard deviation; 19 ± 2%) and SASHA (21 ± 2%; P = 0.086). ECV was higher by MOLLI5(3b)3 (26 ± 2%), MOLLI5(3s)3 (25 ± 2%), and MOLLI5s(3s)3s (25 ± 2%) compared with SASHA or radioisotope (P ≤ 0.001 for all). ECV in volunteers was higher by MOLLI5(3b)3 (26 ± 3%) and MOLLI5(3s)3 (26 ± 3%) than by SASHA (22 ± 3%; P = 0.022 and P = 0.033). No difference was found between MOLLI5s(3s)3s (25 ± 3%) and SASHA (P = 0.225). Native T1 of blood and myocardium as well as postcontrast T1 of myocardium was consistently lower using MOLLI compared with SASHA. ECV increased over time as measured by MOLLI5(3b)3 and MOLLI5(3s)3 for pigs (0.08% and 0.07%/min; P = 0.004 and P = 0.013) and by MOLLI5s(3s)3s for volunteers (0.07%/min; P = 0.032) but did not increase as measured by SASHA.
Conclusion: Clinically available MOLLI and SASHA techniques can be used to accurately estimate ECV in normal myocardium where MOLLI-sequences show minor overestimation driven by underestimation of postcontrast T1 when compared with SASHA. The timing of imaging after contrast administration affected the measurement of ECV using some variants of the MOLLI sequence.
Keywords: ECV; MOLLI; SASHA; T1-mapping; extracellular volume.
© 2019 The Authors. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
H.A. is stockholder in Imacor AB, Lund, Sweden. M.C. and H.E. have received consultancy fees from Imacor AB for analysis of cardiac MRI. No other authors report conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Kruhøffer P. Determination of Inulin in Urine and Plasma. Acta Physiol Scand. 1946;11:1–15.
-
- Tong CY, Prato FS, Wisenberg G, et al. Measurement of the extraction efficiency and distribution volume for Gd‐DTPA in normal and diseased canine myocardium. Magn Reson Med. 1993;30:337–346. - PubMed
-
- Arheden H, Saeed M, Higgins CB, et al. Measurement of the distribution volume of gadopentetate dimeglumine at echo‐planar MR imaging to quantify myocardial infarction: comparison with 99mTc‐DTPA autoradiography in rats. Radiology. 1999;211:698–708. - PubMed
-
- Arheden H, Saeed M, Higgins CB, et al. Reperfused rat myocardium subjected to various durations of ischemia: estimation of the distribution volume of contrast material with echo‐planar MR imaging. Radiology. 2000;215:520–528. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

