Determination of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T upper reference limits under the improved selection criteria in a Chinese population
- PMID: 31418939
- PMCID: PMC6977135
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.23007
Determination of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T upper reference limits under the improved selection criteria in a Chinese population
Abstract
Background: There is no common consensus on how to define the reference population for determination of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin (hs-cTn) upper reference limit (URL). This study aimed to establish 99th percentile URLs of hs-cTnT under both 2018 AACC/IFCC criteria and improved selection criteria for further judging whether two URLs are different.
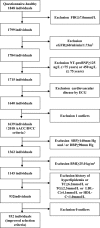
Methods: Applying the stratified cluster sampling protocol, this study took 1848 apparently healthy subjects in communities of Shenyang China as the screening objects. We first followed 2018 AACC/IFCC criteria using surrogate biomarker for diabetes, myocardial dysfunction, renal dysfunction, and electrocardiogram. Then, we followed improved selection criteria to exclude hypertension, overweight and obesity, and dyslipidemia by physical examination and laboratory screening. Accordingly, 99th percentile URLs of hs-cTnT were established.
Results: If the 2018 AACC/IFCC criteria were applied, 99th percentile URLs (90% confidence interval) of hs-cTnT male, female, and total were 19 (17-20) ng/L, 16 (15-17) ng/L, and 18 (16-19) ng/L, respectively. If added a single supplementary selection criteria, 99th percentile URLs of hs-cTnT total reduced to 16 ng/L, 17 ng/L, and 16 ng/L, respectively. If the improved selection criteria were applied, 99th percentile URLs (90% confidence interval) of hs-cTnT male, female, and total were 18 (14-24) ng/L, 13 (11-16) ng/L, and 16 (13-17) ng/L, respectively. The 99th percentile URLs of hs-cTnT male were higher than those of female in every age group.
Conclusions: Improved selection criteria through questionnaire survey, physical examination, and laboratory screening to further exclude hypertension, overweight and obesity, and dyslipidemia can avoid overestimation of the 99th percentile URL of hs-cTnT.
Keywords: 99th percentile; high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T; reference population; selection criteria.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Determination of Age- and Sex-Specific 99th Percentile Upper Reference Limits for High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin I in Healthy Chinese Adults.Cardiology. 2022;147(3):261-270. doi: 10.1159/000523721. Epub 2022 Feb 25. Cardiology. 2022. PMID: 35220311 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of age- and sex-specific 99th percentiles for high-sensitive troponin T from patients: an analytical imprecision- and partitioning-based approach.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2018 Apr 25;56(5):818-829. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2017-0256. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2018. PMID: 29176015
-
Myocardial Injury Thresholds for 4 High-Sensitivity Troponin Assays in U.S. Adults.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2023 May 23;81(20):2028-2039. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2023.03.403. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37197846 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal Detection of Acute Myocardial Injury and Infarction with Cardiac Troponin: Beyond the 99th Percentile, into the High-Sensitivity Era.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2020 Aug 4;22(9):101. doi: 10.1007/s11886-020-01350-w. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32748286 Review.
-
Kinetics, Moderators and Reference Limits of Exercise-Induced Elevation of Cardiac Troponin T in Athletes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Physiol. 2021 Mar 26;12:651851. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.651851. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33841187 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Influence of Age on the Diagnosis of Myocardial Infarction.Circulation. 2022 Oct 11;146(15):1135-1148. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.059994. Epub 2022 Sep 15. Circulation. 2022. PMID: 36106552 Free PMC article.
-
Measurement of Cardiac-Specific Biomarkers in the Emergency Department: New Insight in Risk Evaluation.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 6;24(21):15998. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115998. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Determination of Age- and Sex-Specific 99th Percentile Upper Reference Limits for High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin I in Healthy Chinese Adults.Cardiology. 2022;147(3):261-270. doi: 10.1159/000523721. Epub 2022 Feb 25. Cardiology. 2022. PMID: 35220311 Free PMC article.
-
Age-specific reference values for the 5th generation cardiac troponin T assay in Chinese children.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Mar 18;101(11):e29101. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000029101. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 35356945 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing the Clinical Use of High-Sensitivity Troponin Assays: A Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Dec 30;14(1):87. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14010087. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38201396 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, et al. Fourth universal definition of myocardial infarction (2018). Circulation. 2018;138(20):e618‐e651. - PubMed
-
- Roffi M, Patrono C, Collet J‐P, et al. 2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST‐segment elevation: Task Force for the Management of Acute Coronary Syndromes in Patients Presenting without Persistent ST‐Segment Elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2016;37(3):267‐315. - PubMed
-
- CLSI . Defining, establishing, and verifying reference intervals in the clinical laboratory; approved guideline – third edition. CLSI document C28‐A3c. 2010.
-
- Giannitsis E, Kurz K, Hallermayer K, Jarausch J, Jaffe AS, Katus HA. Analytical validation of a high‐sensitivity cardiac troponin T assay. Clin Chem. 2010;56(2):254‐261. - PubMed
-
- Saenger AK, Beyrau R, Braun S, et al. Multicenter analytical evaluation of a high‐sensitivity troponin T assay. Clin Chim Acta. 2011;412(9‐10):748‐754. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous