Fast serotonin voltammetry as a versatile tool for mapping dynamic tissue architecture: I. Responses at carbon fibers describe local tissue physiology
- PMID: 31419307
- PMCID: PMC7279511
- DOI: 10.1111/jnc.14854
Fast serotonin voltammetry as a versatile tool for mapping dynamic tissue architecture: I. Responses at carbon fibers describe local tissue physiology
Abstract
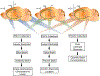
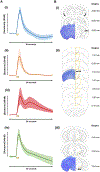
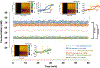
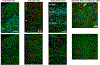
It is important to monitor serotonin neurochemistry in the context of brain disorders. Specifically, a better understanding of biophysical alterations and associated biochemical functionality within subregions of the brain will enable better of understanding of diseases such as depression. Fast voltammetric tools at carbon fiber microelectrodes provide an opportunity to make direct evoked and ambient serotonin measurements in vivo in mice. In this study, we characterize novel stimulation and measurement circuitries for serotonin analyses in brain regions relevant to psychiatric disease. Evoked and ambient serotonin in these brain areas, the CA2 region of the hippocampus and the medial prefrontal cortex, are compared to ambient and evoked serotonin in the substantia nigra pars reticulata, an area well established previously for serotonin measurements with fast voltammetry. Stimulation of a common axonal location evoked serotonin in all three brain regions. Differences are observed in the serotonin release and reuptake profiles between these three brain areas which we hypothesize to arise from tissue physiology heterogeneity around the carbon fiber microelectrodes. We validate this hypothesis mathematically and via confocal imaging. We thereby show that fast voltammetric methods can provide accurate information about local physiology and highlight implications for chemical mapping. Cover Image for this issue: doi: 10.1111/jnc.14739.
Keywords: FSCV; confocal microscopy; hippocampus; medial forebrain bundle; prefrontal cortex; substantia nigra.
© 2019 International Society for Neurochemistry.
Figures



References
-
- Abi-Dargham A, Laruelle M, Aghajanian GK, Charney D and Krystal J (1997) The role of serotonin in the pathophysiology and treatment of schizophrenia. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 9, 1–17. - PubMed
-
- Bremner JD, Narayan M, Anderson ER, Staib LH, Miller HL and Charney DS (2000) Hippocampal volume reduction in major depression. Am J Psychiatry 157, 115–118. - PubMed
-
- Bremner JD, Vythilingam M, Vermetten E, Nazeer A, Adil J, Khan S, Staib LH and Charney DS (2002) Reduced volume of orbitofrontal cortex in major depression. Biol Psychiatry 51, 273–279. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

