Polyphosphate, Zn2+ and high molecular weight kininogen modulate individual reactions of the contact pathway of blood clotting
- PMID: 31420909
- PMCID: PMC6893101
- DOI: 10.1111/jth.14612
Polyphosphate, Zn2+ and high molecular weight kininogen modulate individual reactions of the contact pathway of blood clotting
Abstract
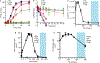
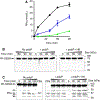
Background: Inorganic polyphosphate modulates the contact pathway of blood clotting, which is implicated in thrombosis and inflammation. Polyphosphate polymer lengths are highly variable, with shorter polymers (approximately 60-100 phosphates) secreted from human platelets, and longer polymers (up to thousands of phosphates) in microbes. We previously reported that optimal triggering of clotting via the contact pathway requires very long polyphosphates, although the impact of shorter polyphosphate polymers on individual proteolytic reactions of the contact pathway was not interrogated.
Objectives and methods: We conducted in vitro measurements of enzyme kinetics to investigate the ability of varying polyphosphate sizes, together with high molecular weight kininogen and Zn2+ , to mediate four individual proteolytic reactions of the contact pathway: factor XII autoactivation, factor XII activation by kallikrein, prekallikrein activation by factor XIIa, and prekallikrein autoactivation.
Results: The individual contact pathway reactions were differentially dependent on polyphosphate length. Very long-chain polyphosphate was required to support factor XII autoactivation, whereas platelet-size polyphosphate significantly accelerated the activation of factor XII by kallikrein, and the activation of prekallikrein by factor XIIa. Intriguingly, polyphosphate did not support prekallikrein autoactivation. We also report that high molecular weight kininogen was required only when kallikrein was the enzyme (ie, FXII activation by kallikrein), whereas Zn2+ was required only when FXII was the substrate (ie, FXII activation by either kallikrein or FXIIa). Activation of prekallikrein by FXIIa required neither Zn2+ nor high molecular weight kininogen.
Conclusions: Platelet polyphosphate and Zn2+ can promote subsets of the reactions of the contact pathway, with implications for a variety of disease states.
Keywords: blood coagulation factors; polyphosphates; prekallikrein; thrombosis; zinc.
© 2019 International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
S.A.S. and J.H.M. are co-inventors on patents and pending patent applications on medical uses of polyP and polyP inhibitors. The research laboratory of J.H.M. receives revenues from sales of polyP and polyP derivatives through Kerafast, Inc. D.G. serves as a consultant and receives consultant’s fees from Bayer AG, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, and Novartis. Y.W. and I.I. declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A site on factor XII required for productive interactions with polyphosphate.J Thromb Haemost. 2023 Jun;21(6):1567-1579. doi: 10.1016/j.jtha.2023.02.014. Epub 2023 Mar 1. J Thromb Haemost. 2023. PMID: 36863563 Free PMC article.
-
Immobilized transition metal ions stimulate contact activation and drive factor XII-mediated coagulation.J Thromb Haemost. 2012 Oct;10(10):2108-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2012.04890.x. J Thromb Haemost. 2012. PMID: 22905925 Free PMC article.
-
Novel family of insect salivary inhibitors blocks contact pathway activation by binding to polyphosphate, heparin, and dextran sulfate.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013 Dec;33(12):2759-70. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.302482. Epub 2013 Oct 3. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013. PMID: 24092749 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic mechanisms of bradykinin mediated diseases: dysregulation of an innate inflammatory pathway.Adv Immunol. 2014;121:41-89. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800100-4.00002-7. Adv Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24388213 Review.
-
Factor XII in coagulation, inflammation and beyond.Cell Signal. 2018 Nov;51:257-265. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2018.08.006. Epub 2018 Aug 15. Cell Signal. 2018. PMID: 30118759 Review.
Cited by
-
A site on factor XII required for productive interactions with polyphosphate.J Thromb Haemost. 2023 Jun;21(6):1567-1579. doi: 10.1016/j.jtha.2023.02.014. Epub 2023 Mar 1. J Thromb Haemost. 2023. PMID: 36863563 Free PMC article.
-
Model for surface-dependent factor XII activation: the roles of factor XII heavy chain domains.Blood Adv. 2022 May 24;6(10):3142-3154. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021005976. Blood Adv. 2022. PMID: 35086137 Free PMC article.
-
Cationic zinc is required for factor XII recruitment and activation by stimulated platelets and for thrombus formation in vivo.J Thromb Haemost. 2020 Sep;18(9):2318-2328. doi: 10.1111/jth.14964. Epub 2020 Jul 30. J Thromb Haemost. 2020. PMID: 32542960 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Polyphosphate on Leukocyte Function.Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 2022;61:131-143. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-01237-2_6. Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35697939 Review.
-
Kallikrein directly interacts with and activates Factor IX, resulting in thrombin generation and fibrin formation independent of Factor XI.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Jan 19;118(3):e2014810118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2014810118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33397811 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schmaier AH. The contact activation and kallikrein/kinin systems: pathophysiologic and physiologic activities. J Thromb Haemost. 2016;14:28–39. - PubMed
-
- Samuel M, Pixley RA, Villanueva MA, Colman RW, Villanueva GB. Human factor XII (Hageman factor) autoactivation by dextran sulfate. Circular dichroism, fluorescence, and ultraviolet difference spectroscopic studies. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:19691–19697. - PubMed
-
- Long AT, Kenne E, Jung R, Fuchs TA, Renné T. Contact system revisited: an interface between inflammation, coagulation, and innate immunity. J Thromb Haemost. 2016;14:427–437. - PubMed

