Diagnostic accuracy of an algorithm for detecting atrial fibrillation in a wrist-type pulse wave monitor
- PMID: 31420946
- PMCID: PMC8030341
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.13648
Diagnostic accuracy of an algorithm for detecting atrial fibrillation in a wrist-type pulse wave monitor
Abstract
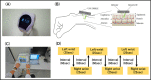
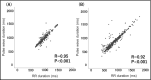
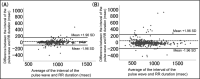
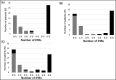
We evaluated the diagnostic value of atrial fibrillation (AF) measured by a wrist-type pulse wave monitor in this case-control study. Six serial pulse wave values (three in the left and three in the right wrist) were measured using a wrist-type monitor in 29 AF patients and 30 subjects with sinus rhythm. We defined "monitor AF in irregular pulse peak (IPP) 15/20/25" as follows: (a) IPP: |interval of pulse peak - the average of the interval of the pulse peak| ≥ the average of the interval of the pulse peak × 15/20/25%; (b) irregular heartbeat (IHB): beats of IPP ≥ total pulse × 20%; and (c) monitor AF: ≥4 IHBs of the six pulse wave measurements. In IPP 15, the sensitivity and specificity were 0.97 and 1.00, respectively. Pulse wave analysis by a wrist-type monitor was shown to have high sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of AF.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; hypertension; pulse wave.
©2019 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
K Kario received research grants from A&D Company Limited; N Yasui, S Takahashi, and K Uemoto are employees of A&D Company Limited; and all other authors report no potential conflict of interest in relation to this article.
This study was conducted as a joint research between Jichi Medical University School of Medicine and A&D Company, Limited.
Figures
References
-
- Go AS, Hylek EM, Phillips KA, et al. Prevalence of diagnosed atrial fibrillation in adults: national implications for rhythm management and stroke prevention: the AnTicoagulation and Risk Factors in Atrial Fibrillation (ATRIA) Study. JAMA. 2001;285:2370‐2375. - PubMed
-
- Heeringa J, van der Kuip D, Hofman A, et al. Prevalence, incidence and lifetime risk of atrial fibrillation: the Rotterdam study. Eur Heart J. 2006;27:949‐953. - PubMed
-
- Wolf PA, Abbott RD, Kannel WB. Atrial fibrillation as an independent risk factor for stroke: the Framingham Study. Stroke. 1991;22:983‐988. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin EJ, Wolf PA, D'Agostino RB, Silbershatz H, Kannel WB, Levy D. Impact of atrial fibrillation on the risk of death: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 1998;98:946‐952. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

