Impact of nanosystems in Staphylococcus aureus biofilms treatment
- PMID: 31420962
- PMCID: PMC8038934
- DOI: 10.1093/femsre/fuz021
Impact of nanosystems in Staphylococcus aureus biofilms treatment
Abstract
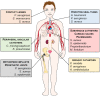
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is considered by the World Health Organization as a high priority pathogen for which new therapies are needed. This is particularly important for biofilm implant-associated infections once the only available treatment option implies a surgical procedure combined with antibiotic therapy. Consequently, these infections represent an economic burden for Healthcare Systems. A new strategy has emerged to tackle this problem: for small bugs, small particles. Here, we describe how nanotechnology-based systems have been studied to treat S. aureus biofilms. Their features, drawbacks and potentialities to impact the treatment of these infections are highlighted. Furthermore, we also outline biofilm models and assays required for preclinical validation of those nanosystems to smooth the process of clinical translation.
Keywords: antibacterial activity; biofilm eradication; drug delivery; nanomedicine; nanotechnology.
© FEMS 2019.
Figures




References
-
- Abed N, Couvreur P. Nanocarriers for antibiotics: a promising solution to treat intracellular bacterial infections. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2014;43:485–96. - PubMed
-
- Abou El-Nour KMM, Eftaiha AA, Al-Warthan Aet al. .. Synthesis and applications of silver nanoparticles. Arabian J Chem. 2010;3:135–40.
-
- Akhil K, Jayakumar J, Gayathri Get al. .. Effect of various capping agents on photocatalytic, antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of ZnO nanoparticles. J Photochem Photobiol B, Biol. 2016;160:32–42. - PubMed
-
- Andersen OZ, Offermanns V, Sillassen Met al. .. Accelerated bone ingrowth by local delivery of strontium from surface functionalized titanium implants. Biomaterials. 2013;34:5883–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

