Targeting the IL-17 Receptor Using Liposomal Spherical Nucleic Acids as Topical Therapy for Psoriasis
- PMID: 31421125
- PMCID: PMC8375607
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jid.2019.06.146
Targeting the IL-17 Receptor Using Liposomal Spherical Nucleic Acids as Topical Therapy for Psoriasis
Abstract
The activation of T helper 17 signaling plays a critical role in psoriasis pathogenesis, and systemically-administered IL-17 inhibitors are highly effective therapy for moderate-to-severe disease. We generated topically-delivered gene-regulating nanoconstructs, comprised of spherically-arrayed antisense DNA (liposomal spherical nucleic acids [L-SNAs]), which are able to penetrate human skin to knock down cutaneous gene targets. Topically-applied L-SNAs targeting the gene encoding the mouse IL-17A receptor (Il17ra) reversed the development of psoriasis clinically, histologically, and transcriptionally in imiquimod-treated psoriasis-like mouse skin. Il17ra L-SNAs reduced the modified PASI by 74% versus controls and decreased epidermal thickness by 56%. Il17ra L-SNA reduced Il17ra protein expression by 75% and significantly decreased the mRNA expression of psoriasis markers, including Defb4, Il17c, S100a7, Pi3, Krt16, and Tnfa versus scrambled spherical nucleic acid (Scr SNA) controls. A human IL17RA L-SNA penetrates 3-dimensional cultures and normal human explants to knock down IL17RA mRNA by 63% and 66%, respectively. After topical application to psoriatic 3-dimensional rafts, anti-human IL17RA L-SNAs reduced the expression of IL17RA (by 72%) and the IL-17-induced genes IL17C (by 85%), DEFB4 (by 83%), TNFA (by 77%), and PI3 (by 65%) versus scrambled L-SNA and vehicle controls (all P < 0.001). Taken together, these data suggest that targeted suppression of IL17RA is a promising new topical treatment strategy for psoriasis.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
BA, WD, DG, RK, SN, AS and RA are employees of Exicure, Inc. AP is a member of the Exicure Scientific Advisory Board and has received Exicure Inc stock options. The other authors state no conflict of interest. This research was supported by a Discovery Grant from National Psoriasis Foundation.
Figures
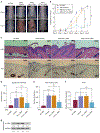
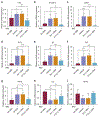
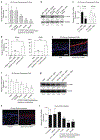
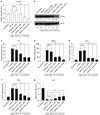
Comment in
-
Spherical Nucleic Acids as Emerging Topical Therapeutics: A Focus on Psoriasis.J Invest Dermatol. 2020 Feb;140(2):278-281. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2019.07.683. J Invest Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 31980061 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boniface K, Bernard FX, Garcia M, Gurney AL, Lecron JC, Morel F. IL-22 inhibits epidermal differentiation and induces proinflammatory gene expression and migration of human keratinocytes. J Immunol 2005;174: 3695e702. - PubMed
-
- Chiricozzi A, Guttman-Yassky E, Suárez-Fariñas M, Nograles KE, Tian S, Cardinale I, et al.Integrative responses to IL-17 and TNF-alpha in human keratinocytes account for key inflammatory pathogenic circuits in psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol 2011;131:677e87. - PubMed
-
- Di Cesare A, Di Meglio P, Nestle FO. The IL-23/Th17 axis in the immuno- pathogenesis of psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol 2009;129:1339e50. - PubMed
-
- Dokter WH, Borger P, Hendriks D, van der Horst I, Halie MR, Vellenga E. Interleukin-4 (IL-4) receptor expression on human T cells is affected by different intracellular signaling pathways and by IL-4 at transcriptional and posttranscriptional level. Blood 1992;80:2721e8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

