Nucleo-cytoplasmic Partitioning of ARF Proteins Controls Auxin Responses in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 31421981
- PMCID: PMC6778021
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.06.044
Nucleo-cytoplasmic Partitioning of ARF Proteins Controls Auxin Responses in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
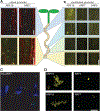
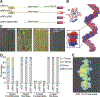
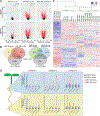
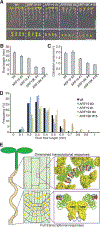
The phytohormone auxin plays crucial roles in nearly every aspect of plant growth and development. The auxin response factor (ARF) transcription factor family regulates auxin-responsive gene expression and exhibits nuclear localization in regions of high auxin responsiveness. Here we show that the ARF7 and ARF19 proteins accumulate in micron-sized assemblies within the cytoplasm of tissues with attenuated auxin responsiveness. We found that the intrinsically disordered middle region and the folded PB1 interaction domain of ARFs drive protein assembly formation. Mutation of a single lysine within the PB1 domain abrogates cytoplasmic assemblies, promotes ARF nuclear localization, and results in an altered transcriptome and morphological defects. Our data suggest a model in which ARF nucleo-cytoplasmic partitioning regulates auxin responsiveness, providing a mechanism for cellular competence for auxin signaling.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

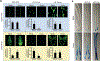
References
-
- Boer DR, Freire-Rios A, van den Berg WA, Saaki T, Manfield IW, Kepinski S, López-Vidrieo I, Franco-Zorrilla JM, de Vries SC, Solano R, et al. (2014). Structural Basis for DNA Binding Specificity by the Auxin-Dependent ARF Transcription Factors. Cell 156, 577–589. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

