How I treat ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 31423342
- PMCID: PMC6677959
- DOI: 10.1136/esmoopen-2019-000524
How I treat ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
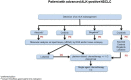
Since the discovery of anaplastic lymphocyte kinase (ALK) rearrangement in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and subsequent development of increasingly effective and central nervous system (CNS)-penetrant first-generation, second-generation and third-generation ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), the landscape of resistance mechanisms and treatment decisions has become increasingly complex. Tissue and/or plasma-based molecular tests can identify not only the rearrangement proper but also common resistance mechanisms to guide decision-making for further lines of treatment. However, frequently encountered questions exist regarding how to diagnosis ALK rearrangement, how to select a first-line ALK TKI, how to diagnose and manage ALK TKI resistance, how to control CNS disease and how to handle failure of ALK inhibition. Herein, we attempt to answer these questions through the evidence-based interpretation of studies on ALK-rearranged NSCLC combined with experience gained from our institution. The authors also propose a therapeutic algorithm for the management of this complex and highly treatable disease to assist clinicians globally in the treatment of patients with ALK-positive NSCLC.
Keywords: ALK; NSCLC; acquired resistance; alectinib; ceritinib; crizotinib; lorlatinib.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: CR reports personal fees from Novartis, personal fees from MSD, non-financial support from OncoDNA, personal fees and non-financial support from GuardantHealth, outside the submitted work. RM reports research fuding from Astra Zeneca and consulation for Genentech. All other authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures
References
-
- Lindeman NI, Cagle PT, Aisner DL, et al. . Updated molecular testing guideline for the selection of lung cancer patients for treatment with targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors: guideline from the College of American Pathologists, the International Association for the study of lung cancer, and the Association for molecular pathology. J Mol Diagn 2018;20:129–59. 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2017.11.004 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources