cGMP-dependent protein kinase I in vascular smooth muscle cells improves ischemic stroke outcome in mice
- PMID: 31423931
- PMCID: PMC6893979
- DOI: 10.1177/0271678X19870583
cGMP-dependent protein kinase I in vascular smooth muscle cells improves ischemic stroke outcome in mice
Abstract
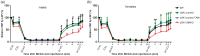
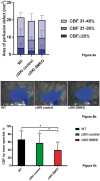
Recent works highlight the therapeutic potential of targeting cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)-dependent pathways in the context of brain ischemia/reperfusion injury (IRI). Although cGMP-dependent protein kinase I (cGKI) has emerged as a key mediator of the protective effects of nitric oxide (NO) and cGMP, the mechanisms by which cGKI attenuates IRI remain poorly understood. We used a novel, conditional cGKI knockout mouse model to study its role in cerebral IRI. We assessed neurological deficit, infarct volume, and cerebral perfusion in tamoxifen-inducible vascular smooth muscle cell-specific cGKI knockout mice and control animals. Stroke experiments revealed greater cerebral infarct volume in smooth muscle cell specific cGKI knockout mice (males: 96 ± 16 mm3; females: 93 ± 12 mm3, mean±SD) than in all control groups: wild type (males: 66 ± 19; females: 64 ± 14), cGKI control (males: 65 ± 18; females: 62 ± 14), cGKI control with tamoxifen (males: 70 ± 8; females: 68 ± 10). Our results identify, for the first time, a protective role of cGKI in vascular smooth muscle cells during ischemic stroke injury. Moreover, this protective effect of cGKI was found to be independent of gender and was mediated via improved reperfusion. These results suggest that cGKI in vascular smooth muscle cells should be targeted by therapies designed to protect brain tissue against ischemic stroke.
Keywords: Cerebral blood flow; cGMP-dependent protein kinase I; ischemia–reperfusion injury; middle cerebral artery occlusion-reperfusion model; stroke.
Figures




References
-
- Francis SH, Corbin JD. Cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases: intracellular receptors for cAMP and cGMP Action. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 1999; 36: 275–328. - PubMed
-
- Zhang R, Wang L, Zhang L, et al. Nitric oxide enhances angiogenesis via the synthesis of vascular endothelial growth factor and cGMP after stroke in the rat. Circ Res 2003; 92: 308–313. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Wang N, Liu Y, et al. Yonkenafil: a novel phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor induces neuronal network potentiation by a cGMP-dependent Nogo-R axis in acute experimental stroke. Exp Neurol 2014; 261: 267–277. - PubMed
-
- Pilz RB, Broderick KE. Role of cyclic GMP in gene regulation. Front Biosci 2005; 10: 1239–1268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

