Ethical case interventions for adult patients
- PMID: 31424106
- PMCID: PMC6698942
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012636.pub2
Ethical case interventions for adult patients
Abstract
Background: Decisions in clinical medicine can be associated with ethical challenges. Ethical case interventions (e.g. ethics committee, moral case deliberation) identify and analyse ethical conflicts which occur within the context of care for patients. Ethical case interventions involve ethical experts, different health professionals as well as the patient and his/her family. The aim is to support decision-making in clinical practice. This systematic review gathered and critically appraised the available evidence of controlled studies on the effectiveness of ethical case interventions.
Objectives: To determine whether ethical case interventions result in reduced decisional conflict or moral distress of those affected by an ethical conflict in clinical practice; improved patient involvement in decision-making and a higher quality of life in adult patients. To determine the most effective models of ethical case interventions and to analyse the use and appropriateness of the outcomes in experimental studies.
Search methods: We searched the following electronic databases for primary studies to September 2018: CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase, CINAHL and PsycINFO. We also searched CDSR and DARE for related reviews. Furthermore, we searched Clinicaltrials.gov, International Clinical Trials Registry Platform Search Portal and conducted a cited reference search for all included studies in ISI WEB of Science. We also searched the references of the included studies.
Selection criteria: We included randomised trials, non-randomised trials, controlled before-after studies and interrupted time series studies which compared ethical case interventions with usual care or an active control in any language. The included population were adult patients. However, studies with mixed populations consisting of adults and children were included, if a subgroup or sensitivity analysis (or both) was performed for the adult population.
Data collection and analysis: We used standard methodological procedures expected by Cochrane and the Effective Practice and Organisation of Care review group. We used meta-analysis based on a random-effects model for treatment costs and structured analysis for the remaining outcomes, because these were heterogeneously reported. We used the GRADE approach to assess the certainty of the evidence.
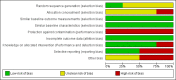
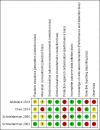
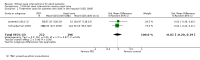
Main results: We included four randomised trials published in six articles. The publication dates ranged from 2000 to 2014. Three studies were conducted in the USA, and one study in Taiwan. All studies were conducted on intensive care units and included 1165 patients. We judged the included studies to be of moderate or high risk of bias. It was not possible to compare different models of the intervention regarding effectiveness due to the diverse character of the interventions and the small number of studies. Included studies did not directly measure the main outcomes. All studies received public funding and one received additional funding from private sources.We identified two models of ethical case interventions: proactive and request-based ethics consultation. Three studies evaluated proactive ethics consultation (n = 1103) of which one study reported findings on one key outcome criterion. The studies did not report data on decisional conflict, moral distress of participants of ethical case interventions, patient involvement in decision-making, quality of life or ethical competency for proactive ethics consultation. One study assessed satisfaction with care on a 5-point Likert scale (1 = lowest rating, 5 = highest rating). The healthcare providers (nurses and physicians, n = 365) scored a value of 4 or 5 for 81.4% in the control group and 86.1% in the intervention group (P > 0.05). The patients or their surrogates (n = 275) scored a value of 4 or 5 for 83.6% in the control group and for 74.8% in the intervention group (P > 0.05). It was uncertain whether proactive ethics consultation led to high satisfaction with care, because the certainty of evidence was very low.One study evaluated request-based ethics consultation (n = 62). The study indirectly measured decisional conflict by assessing consensus regarding patient care. The risk (increase in consensus, reduction in decisional conflict) increased by 80% as a result of the intervention. The risk ratio was 0.20 (95% confidence interval 0.09 to 0.46; P < 0.01). It was uncertain whether request-based ethics consultation reduced decisional conflict, because the certainty of evidence was very low. The study did not report data on moral distress of participants of ethical case interventions, patient involvement in decision-making, quality of life, or ethical competency or satisfaction with care for request-based ethics consultation.
Authors' conclusions: It is not possible to determine the effectiveness of ethical case interventions with certainty due to the low certainty of the evidence of included studies in this review. The effectiveness of ethical case interventions should be investigated in light of the outcomes reported in this systematic review. In addition, there is need for further research to identify and measure outcomes which reflect the goals of different types of ethical case intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
CB: none known.
MG: none known.
JH: none known.
JS: none known.
JV: none known.
SN: none known.
Figures

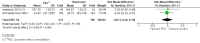


Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Andereck 2014 {published data only}
Chen 2014 {published data only}
Schneiderman 2000 {published data only}
Schneiderman 2003 {published data only}
-
- Cohn F, Goodman‐Crews P, Rudman W, Schneiderman LJ, Waldman E. Proactive ethics consultation in the ICU. A comparison of value perceived by healthcare professionals and recipients. Journal of Clinical Ethics 2007;18(2):140‐7. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality 2003 {published data only}
-
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ). Ethics consultations can help resolve conflicts that may prolong unwanted or nonbeneficial ICU treatments. AHRQ Research Activities 2003;280:6.
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality 2005 {published data only}
-
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ). Ethics consultations can reduce nonbeneficial treatments and costs among dying patients. AHRQ Research Activities 2005;301:23‐24.
Boisaubin 1999 {published data only}
-
- Boisaubin EV, Carter MA. Optimizing ethics services and education in a teaching hospital: rounds versus consultation. Journal of Clinical Ethics 1999;10(4):294‐9. - PubMed
Chromik 2008 {published data only}
-
- Chromik AM, Wemhöner T, Sülberg D, Reploh KG, Laubental H, Uhl W, Mittelkötter U. Interdisciplinary ethics consultation on the surgical intensive care unit [Das interdisziplinäre Ethikkonsil auf der operativen Intensivstation]. Zentralblatt für Chirurgie 2008;133(3):285‐91. [DOI: 10.1055/s-2008-1076825] - DOI - PubMed
Cooke 2001 {published data only}
-
- Cooke M. Ethics consultations in the intensive care unit (ICU) reduced duration of ICU stay and time on aggressive, life sustaining treatments with no change in overall mortality. Evidence Based Nursing 2001;4(4):119. [DOI: 10.1136/ebn.4.4.119] - DOI
Dowdy 1998 {published data only}
-
- Dowdy MD, Robertson C, Bander JA. A study of proactive ethics consultation for critically and terminally ill patients with extended lengths of stay. Critical Care Medicine 1998;26(2):252‐9. - PubMed
Hamel 2006 {published data only}
-
- Hamel R. Ethics committees pursuing enhanced effectiveness. Health Progress 2006;87(2):17.
Heilicser 2000 {published data only}
-
- Heilicser BJ, Meltzer D, Siegler M. The effect of clinical medical ethics consultation on healthcare costs. Journal of Clinical Ethics 2000;11(1):31‐8. - PubMed
Helft 2014 {published data only}
-
- Helft PR. Consultations in Ethics. Oncology 2014;28(9):811‐12. - PubMed
Jones 2004 {published data only}
-
- Jones T. Ethics consultations reduced hospital, ICU, and ventilation days in patients who died before hospital discharge in the ICU. Evidence Based Nursing 2004;7(2):53. [DOI: ] - PubMed
Kamat 2012 {published data only}
-
- Kamat S, Rajendram P, Shuman A, Voigt L, Kostelecky N, McCabe M, et al. A contemporary analysis of ethics consultations in an oncologic icu. Chest 2012;142(4_MeetingAbstracts):759A. [DOI: 10.1378/chest.1389264] - DOI
Katz 2010 {published data only}
LaPuma 1995 {published data only}
-
- LaPuma J. Satisfying managed care patients through ethics consultation. Managed Care 1995;4(10):53‐4. - PubMed
Lindon 1996 {published data only}
Lueders 1990 {published data only}
-
- Lueders AJ. An evaluation of ethical decision‐making. Journal of the Arkansas Medical Society 1990;86(8):307‐8. - PubMed
McClung 1997 {published data only}
-
- McClung JA. Evaluating an ethics consultation service.. American Journal of Medicine 1997;103(2):167‐8. - PubMed
Miller 1996 {published data only}
-
- Miller J. Ethics case consultation: a study in processes. Massachusetts Nurse 1996;66(9):5.
Nelson 2004 {published data only}
-
- Nelson LJ. Ethics consultations reduce time and procedures in intensive care. Evidence‐Based Healthcare 2004;8(2):63‐4. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ehbc.2004.02.010] - DOI
Nursing Economics Data Bank 2006 {published data only}
-
- Nursing Economics Data Bank. Ethics consultations can reduce nonbeneficial treatments and costs among dying patients. Nursing Economics 2006;24(3):165.
Orr 2009 {published data only}
-
- Orr RD, Shelton W. A process and format for clinical ethics consultation. Journal of Clinical Ethics 2009;20(1):79‐89. - PubMed
Palmer 2004 {published data only}
-
- Palmer K. Doing the right thing. Hospitals ethics committees help clinicians, families, and facilities wrestle with tough questions. A process and format for clinical ethics consultation. Minnesota Medicine 2004;87(6):26‐9. - PubMed
Perkins 1993 {published data only}
Perkins 2004 {published data only}
-
- Perkins HS. Ethics consultation reduced hospital, ICU, and ventilation days for ICU patients who died before hospital discharge. ACP Journal Club 2004;140(2):36. - PubMed
Quigley 2003 {published data only}
Ranisch 2016 {published data only}
Relias Media 1999 {published data only}
-
- Relias Media. Ethics can coexist with corporate compliance: integrity approach can be more cost‐effective. Healthcare Risk Management 1999;21(1):6‐11.
Robles 1999 {published data only}
Rollins 2003 {published data only}
-
- Rollins G. Ethics consultations reduce futile life‐sustaining treatments. Report on Medical Guidelines and Outcomes Research 2003;14(19):9‐10. - PubMed
Schneiderman 2002 {published data only}
Schneiderman 2005 {published data only}
Schneiderman 2006 {published data only}
Schwalbe 2007 {published data only}
-
- Schwalbe B. Ethics consultation in the intensive care unit [Ethikberatung auf der Intensivstation]. Journal für Anästhesie und Intensivbehandlung 2007;14(1):188.
Silberman 2007 {published data only}
Additional references
Ackermann 2016
-
- Ackermann S, Balsiger L, Salathé M. [Ethikstrukturen an Akutspitälern, Psychiatrischen Kliniken und Rehabilitationskliniken der Schweiz. Dritte, erweiterte Umfrage der Schweizerischen Akademie der Medizinischen Wissenschaften]. Bioethica Forum 2016;9(2):52‐9.
Au 2018
Aulisio 2000
-
- Aulisio MP, Arnold RM, Youngner SJ. Health care ethics consultation: nature, goals, and competencies. A position paper from the Society for Health and Human Values‐Society for Bioethics Consultation Task Force on Standards for Bioethics Consultation. Annals of Internal Medicine 2000;133(1):59‐69. [DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-133-1-200007040-00012] - DOI - PubMed
Bacchetta 1997
Beca 2010
-
- Beca JP, Koppmann A, Chavez P, Delgado I, Solar S. Analysis of a clinical ethics consultation experience in intensive care [Análisis de una experiencia de consultoría ético clínica en cuidado intensivo]. Revista Médica de Chile 2010;138(7):815‐20. [DOI: 10.4067/S0034-98872010000700004] - DOI - PubMed
Braunack‐Mayer 2001
Chen 2008
Cohn 2007
-
- Cohn F, Goodman‐Crews P, Rudman W, Schneiderman LJ, Waldman E. Proactive ethics consultation in the ICU. A comparison of value perceived by healthcare professionals and recipients. Journal of Clinical Ethics 2007;18(2):140‐7. - PubMed
Corley 2001
-
- Corley MC, Elswick RK, Gorman M, Clor T. Development and evaluation of a moral distress scale. Journal of Advanced Nursing 2011;33(2):250‐6. - PubMed
Covidence [Computer program]
-
- Veritas Health Innovation. Covidence. Melbourne, Australia: Veritas Health Innovation, Accessed 1 September 2018.
Craig 2006
-
- Craig JM, May T. Evaluating the outcomes of ethics consultation. Journal of Clinical Ethics 2006;17(2):168‐80. - PubMed
Detering 2010
EPOC 2013
-
- Cochrane Effective Practice, Organisation of Care (EPOC). Data collection form. EPOC Resources for review authors. Oslo: Norwegian Knowledge Centre for the Health Services 2013. Available at: epoc.cochrane.org/resources/epoc‐resources‐review‐authors.
EPOC 2015
-
- Cochrane Effective Practice, Organisation of Care (EPOC). Suggested risk of bias criteria for EPOC reviews. EPOC Resources for review authors. Oslo: Norwegian Knowledge Centre for the Health Services 2015. Available at: epoc.cochrane.org/resources/epoc‐resources‐review‐authors.
EPOC 2017a
-
- Cochrane Effective Practice, Organisation of Care (EPOC). Search audit template excel spreadsheet. EPOC Resources for review authors. Oslo: Norwegian Knowledge Centre for the Health Services 2017. Available at: epoc.cochrane.org/resources/epoc‐resources‐review‐authors.
EPOC 2017b
-
- Cochrane Effective Practice, Organisation of Care (EPOC). EPOC worksheets for preparing a summary of findings using GRADE. EPOC Resources for review authors. Oslo: Norwegian Knowledge Centre for the Health Services 2017. Available at: epoc.cochrane.org/resources/epoc‐resources‐review‐authors.
EPOC 2017c
-
- Cochrane Effective Practice, Organisation of Care (EPOC). Worksheet 4: key messages in plain language. EPOC worksheets for preparing a summary of findings using GRADE. EPOC Resources for review authors. Oslo: Norwegian Knowledge Centre for the Health Services 2017. Available at: epoc.cochrane.org/resources/epoc‐resources‐review‐authors.
Fletcher 1996
-
- Fletcher JC, Siegler M. What are the goals of ethics consultation? A consensus statement. Journal of Clinical Ethics 1996;7(2):122‐6. - PubMed
Forde 2011
Fox 1996a
-
- Fox E, Arnold RM. Evaluating outcomes in ethics consultation research. Journal of Clinical Ethics 1996;7(2):127‐38. - PubMed
Fox 1996b
-
- Fox E. Concepts in evaluation applied to ethics consultation research. Journal of Clinical Ethics 1996;7(2):116‐21. - PubMed
Fox 2007
Gather 2019
-
- Gather J, Kaufmann S, Otte I, Juckel G, Schildmann J, Vollmann J. Level of development of clinical ethics consultation in psychiatry. Results of a survey among psychiatric acute clinics and forensic psychiatric hospitals [Entwicklungsstand von klinischer Ethikberatung in der Psychiatrie]. Psychiatrische Praxis 2019; Vol. 46, issue 2:90‐6. [DOI: 10.1055/a-0579-6469] - DOI - PubMed
German Medical Association 2006
-
- German Medical Association. [Stellungnahme der Zentralen Kommission zur Wahrung ethischer Grundsätze in der Medizin und ihren Grenzgebieten (Zentrale Ethikkommission) bei der Bundesärztekammer zur Ethikberatung in der klinischen Medizin]. Deutsches Ärzteblatt 2006;103(24):1703‐7.
Gilmer 2005
GRADEpro GDT [Computer program]
-
- McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime). GRADEpro GDT. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime), 2015.
Hajibabaee 2016
Hem 2015
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Hoffmann 1993
Hoffmann 2014
Huffman 2012
Hurst 2007
JCAHO 2005
-
- Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO). Comprehensive Accreditation Manual for Hospitals. Oakbrook Terrace (IL): Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO), 2005.
Kalager 2011
Kaposy 2016
Kirkham 2010
Kristjanson 1993
La Puma 1988
La Puma 1992
Lamiani 2015
Landeweer 2011
Liberati 2009
Lo 2003
Mack 2012
McCarthy 2015
McClung 1996
Melbourne 2010
Molewijk 2008
O'Connor 1995
-
- O'Connor AM. Validation of a decisional conflict scale. Medical Decision Making 1995;15(1):25‐30. - PubMed
Oh 2015
Orr 1996
Pedersen 2010
-
- Pedersen R, Hurst SA, Schildmann J, Schuster S, Molewijk B. The development of a descriptive evaluation tool for clinical ethics case consultations. Clinical Ethics 2010;5(3):136‐41. [DOI: ]
Pfäfflin 2009
Pope 2011
-
- Pope TM. Legal briefing: healthcare ethics committees. Journal of Clinical Ethics 2011;22(1):74‐93. - PubMed
Reiter‐Theil 2014
Review Manager 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Rogers 2008
Royal College of Physicians 2005
-
- Royal College of Physicians of London. Ethics in Practice. Background and Recommendations for Enhanced Support. Report of a Working Party. London (UK): Royal College of Physicians of London, 2005.
Rushton 2013
Salloch 2016
-
- Salloch S, Ritter P, Wäscher S, Vollmann J, Schildmann J. What is an ethical problem and how do I find it? Theoretical, methodological and practical questions to identify ethical problems in an empirical–ethical intervention study [Was ist ein ethisches Problem und wie finde ich es? Theoretische, methodologische und forschungspraktische Fragen der Identifikation ethischer Probleme am Beispiel einer empirisch‐ethischen Interventionsstudie]. Ethik in der Medizin 2016; Vol. 28, issue 4:267‐81. [DOI: 10.1007/s00481-016-0384-x] - DOI
Schildmann 2010
-
- Schildmann J, Vollmann J. Evaluation of clinical ethics consultation: a systematic review and critical appraisal of research methods and outcome criteria. In: Schildmann J, Gordon J‐S, Vollmann J editor(s). Clinical Ethics Consultation: Theories and Methods, Implementation, Evaluation. 1st Edition. Farnham (UK): Ashgate, 2010:203‐15.
Schildmann 2013
Schildmann 2016
-
- Schildmann J, Nadolny S, Wäscher S, Gysels M, Vollmann J, Bausewein C. Clinical ethics support services (CESS) as complex intervention. Preliminary findings of a conceptual analysis and possible implications for outcomes research. Bioethica Forum 2016;9(2):90‐3.
Schildmann 2019
-
- Schildmann J, Nadolny S, Haltaufderheide J, Gysels M, Vollmann J, Bausewein C. Do we understand the intervention? What complex intervention research can teach us for the evaluation of Clinical Ethics Support Services (CESS). BMC Medical Ethics 2019; Vol. 20:48. [DOI: 10.1186/s12910-019-0381-y] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Schochow 2015
Slowther 2012
Steinkamp 2007
Strech 2010
Strätling 2013
Swiss Academy of Medical Sciences 2012
-
- Swiss Academy of Medical Sciences. Ethics Support in Medicine. www.samw.ch (accessed 1 March 2019).
Tanner 2014
-
- Tanner S, Albisser‐Schleger H, Meyer‐Zehnder B, Schnurrer V, Reiter‐Theil S, Pargger H. Clinical everyday ethics‐support in handling moral distress? Evaluation of an ethical decision‐making model for interprofessional clinical teams [Klinische Alltagsethik – Unterstützung im Umgang mit moralischem Disstress? Evaluation eines ethischen Entscheidungsfindungsmodells für interprofessionelle klinische Teams]. Medizinische Klinik, Intensivmedizin und Notfallmedizin 2014;109(5):354‐63. [DOI: 10.1007/s00063-013-0327-y] - DOI - PubMed
Tarzian 2013
-
- Tarzian AJ, ASBH Core Competencies Update Task Force. Health care ethics consultation: an update on core competencies and emerging standards from the American Society for Bioethics and Humanities' Core Competencies Update Task Force. American Journal of Bioethics 2013;13(2):3‐13. [DOI: 10.1080/15265161.2012.750388] - DOI - PubMed
Tulsky 1996
-
- Tulsky JA, Fox E. Evaluating ethics consultation: framing the questions. Journal of Clinical Ethics 1996;7(2):109‐15. - PubMed
Wan 2014
Ware 2001
-
- Ware JE Jr. SF‐36 Physical and Mental Health Summary Scales: a Manual for Users of Version 1. 2nd Edition. Lincoln: Quality Metric Inc, 2001.
Wenger 2002
White 1993
Whitehead 2009
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

