Discovery and Development of Anti-HIV Therapeutic Agents: Progress Towards Improved HIV Medication
- PMID: 31424371
- PMCID: PMC7132033
- DOI: 10.2174/1568026619666190712204603
Discovery and Development of Anti-HIV Therapeutic Agents: Progress Towards Improved HIV Medication
Abstract
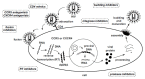
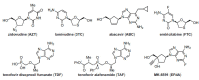
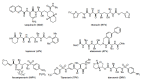
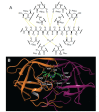
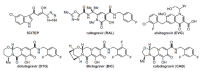
The history of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)/AIDS therapy, which spans over 30 years, is one of the most dramatic stories of science and medicine leading to the treatment of a disease. Since the advent of the first AIDS drug, AZT or zidovudine, a number of agents acting on different drug targets, such as HIV enzymes (e.g. reverse transcriptase, protease, and integrase) and host cell factors critical for HIV infection (e.g. CD4 and CCR5), have been added to our armamentarium to combat HIV/AIDS. In this review article, we first discuss the history of the development of anti-HIV drugs, during which several problems such as drug-induced side effects and the emergence of drug-resistant viruses became apparent and had to be overcome. Nowadays, the success of Combination Antiretroviral Therapy (cART), combined with recently-developed powerful but nonetheless less toxic drugs has transformed HIV/AIDS from an inevitably fatal disease into a manageable chronic infection. However, even with such potent cART, it is impossible to eradicate HIV because none of the currently available HIV drugs are effective in eliminating occult "dormant" HIV cell reservoirs. A number of novel unique treatment approaches that should drastically improve the quality of life (QOL) of patients or might actually be able to eliminate HIV altogether have also been discussed later in the review.
Keywords: AIDS; Combination antiretroviral therapy; HIV; Integrase inhibitors; Protease inhibitors; Reverse transcriptase inhibitors..
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Figures






References
-
- Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J.C., Rey F., Nugeyre M.T., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Dauguet C., Axler-Blin C., Vézinet-Brun F., Rouzioux C., Rozenbaum W., Montagnier L. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983;220(4599):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6189183. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gallo R.C., Sarin P.S., Gelmann E.P., Robert-Guroff M., Richardson E., Kalyanaraman V.S., Mann D., Sidhu G.D., Stahl R.E., Zolla-Pazner S., Leibowitch J., Popovic M. Isolation of human T-cell leukemia virus in acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983;220(4599):865–867. doi: 10.1126/science.6601823. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mitsuya H., Weinhold K.J., Furman P.A., St Clair M.H., Lehrman S.N., Gallo R.C., Bolognesi D., Barry D.W., Broder S. 3′-Azido-3′-deoxythymidine (BW A509U): An antiviral agent that inhibits the infectivity and cytopathic effect of human T-lymphotropic virus type III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1985;82(20):7096–7100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7096. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yarchoan R., Klecker R.W., Weinhold K.J., Markham P.D., Lyerly H.K., Durack D.T., Gelmann E., Lehrman S.N., Blum R.M., Barry D.W. Administration of 3′-azido-3′-deoxythymidine, an inhibitor of HTLV-III/LAV replication, to patients with AIDS or AIDS-related complex. Lancet. 1986;1(8481):575–580. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(86)92808-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
