A New Perspective on Dry Eye Classification: Proposal by the Asia Dry Eye Society
- PMID: 31425351
- PMCID: PMC7423530
- DOI: 10.1097/ICL.0000000000000643
A New Perspective on Dry Eye Classification: Proposal by the Asia Dry Eye Society
Erratum in
-
A New Perspective on Dry Eye Classification: Proposal by the Asia Dry Eye Society: Erratum.Eye Contact Lens. 2020 Sep;46(5):e39. doi: 10.1097/ICL.0000000000000742. Eye Contact Lens. 2020. PMID: 32842076 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
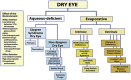
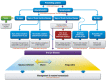
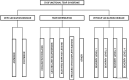
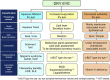
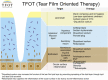
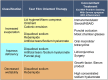
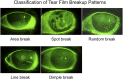
The 2017 consensus report of the Asia Dry Eye Society (ADES) on the definition and diagnosis of dry eyes described dry eye disease as "Dry eye is a multifactorial disease characterized by unstable tear film causing a variety of symptoms and/or visual impairment, potentially accompanied by ocular surface damage." The report emphasized the instability of tear film and the importance of visual dysfunction in association with dry eyes, highlighting the importance of the evaluation of tear film stability. This report also discussed the concept of tear film-oriented therapy, which stemmed from the definition, and which is centered on provision of insufficient components in each tear film layer and ocular surface epithelium. The current ADES report proposes a simple classification of dry eyes based on the concept of tear film-oriented diagnosis and suggests that there are three types of dry eye: aqueous-deficient, decreased wettability, and increased evaporation. It is suggested that these three types respectively coincide with the problems of each layer: aqueous, membrane-associated mucins, and lipid/secretory mucin. Although each component cannot be quantitatively evaluated with the current technology, a practical diagnosis based on the patterns of fluorescein breakup is recommended. The Asia Dry Eye Society classification report suggests that for a practical use of the definition, diagnostic criteria and classification system should be integrated and be simple to use. The classification system proposed by ADES is a straightforward tool and simple to use, only through use of fluorescein, which is available even to non-dry eye specialists, and which is believed to contribute to an effective diagnosis and treatment of dry eyes.
Conflict of interest statement
Outside the submitted work, these authors report COI as follows: K. Tsubota reports research funding and consultancies from Santen Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd and Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd, and holds the patent right for the method and apparatus used for the functional visual acuity measurement system (US patent no: 7470026 by Kowa Company); and is a consultant for Shire. N. Yokoi reports personal fees from Santen Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd, Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd, and consultancies from Rhoto Co, Ltd, Alcon Japan Co, Ltd, and patents for ophthalmologic apparatus with Kowa Co, Ltd. H. Watanabe reports personal fees from Santen Pharmaceutical Co Ltd, Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd, Senju Pharmaceutical, Alcon and Pfizer Inc. M. Dogru reports personal fees from Echo Electricity, Santen Pharmaceutical, and Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd. T. Kojima reports personal fees from Staar Surgical, Santen Pharmaceutical, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Johnson & Johnson, and Alcon. M. Yamada reports research funding from Santen Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd, and personal fees from Santen Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd, Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd, Johnson & Johnson Vision Care Co, and Alcon Co. S. Kinoshita reports research funding and consultancies from Santen Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd, Senju Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd, and KOWA Co, Ltd, research funding from Oncolys Biopharma Inc, HOYA Corporation, and Lion Corporation, personal fees from Alcon Japan and AMO Inc. J. Y. Hyon reports researching funding and consultancy with Santen Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd. K. C. Yoon reports research funding and consultancies from Santen Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd and Pfizer. K. Y. Seo reports personal fees from Santen Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd and Lumenis Korea Ltd. L. Tong reports funding for research, advisory boards and conference related travels from Alcon-Novartis, Allergan, Bausch and Lomb, and Santen Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd. V. Puangsricharern reports honorarium as a speaker for Santen, Alcon and Allergan. R. Lim-Bon-Siong is a member of the Santen Advisory Board and receives educational and research grants from Santen Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd. T. K. Yong received travel grants from Santen and Allergan. Z. Liu reports research funding or consultancies or travel grants from: Alcon, Allergen, Novartis Johnson & Johnson Vision, Santen, Senju, Yuejia, Xingqi, Zhuhaiyisheng, Reilin, Dakai. J. Shimazaki reports research funding and consultancies from Santen Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd and Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd. The remaining authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Tsubota K, Yokoi N, Shimazaki J, et al. New perspectives on dry eye definition and diagnosis: A consensus report by the Asia dry eye society. Ocul Surf 2017;15:65–76. - PubMed
-
- Goto T, Zheng X, Okamoto S, et al. Tear film stability analysis system: Introducing a new application for videokeratography. Cornea 2004;23:S65–S70. - PubMed
-
- Kaido M, Ishida R, Dogru M, et al. The relation of functional visual acuity measurement methodology to tear functions and ocular surface status. Jpn J Ophthalmol 2011;55:451–459. - PubMed
-
- Kojima T, Ishida R, Dogru M, et al. A new noninvasive tear stability analysis system for the assessment of dry eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2004;45:1369–1374. - PubMed
-
- Kinoshita S, Awamura S, Oshiden K, et al. Rebamipide (OPC-12759) in the treatment of dry eye: A randomized, double-masked, multicenter, placebo-controlled phase II study. Ophthalmology 2012;119:2471–2478. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

