Factors in the disease severity of ATP1A3 mutations: Impairment, misfolding, and allele competition
- PMID: 31425744
- PMCID: PMC7397496
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.104577
Factors in the disease severity of ATP1A3 mutations: Impairment, misfolding, and allele competition
Abstract
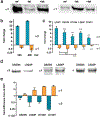
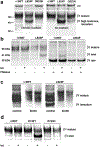
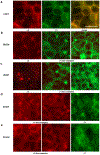
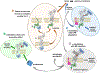
Dominant mutations of ATP1A3, a neuronal Na,K-ATPase α subunit isoform, cause neurological disorders with an exceptionally wide range of severity. Several new mutations and their phenotypes are reported here (p.Asp366His, p.Asp742Tyr, p.Asp743His, p.Leu924Pro, and a VUS, p.Arg463Cys). Mutations associated with mild or severe phenotypes [rapid-onset dystonia-parkinsonism (RDP), alternating hemiplegia of childhood (AHC), or early infantile epileptic encephalopathy (EIEE)] were expressed in HEK-293 cells. Paradoxically, the severity of human symptoms did not correlate with whether there was enough residual activity to support cell survival. We hypothesized that distinct cellular consequences may result not only from pump inactivation but also from protein misfolding. Biosynthesis was investigated in four tetracycline-inducible isogenic cell lines representing different human phenotypes. Two cell biological complications were found. First, there was impaired trafficking of αβ complex to Golgi apparatus and plasma membrane, as well as changes in cell morphology, for two mutations that produced microcephaly or regions of brain atrophy in patients. Second, there was competition between exogenous mutant ATP1A3 (α3) and endogenous ATP1A1 (α1) so that their sum was constant. This predicts that in patients, the ratio of normal to mutant ATP1A3 proteins will vary when misfolding occurs. At the two extremes, the results suggest that a heterozygous mutation that only impairs Na,K-ATPase activity will produce relatively mild disease, while one that activates the unfolded protein response could produce severe disease and may result in death of neurons independently of ion pump inactivation.
Keywords: Ataxia; Cytopathology; Dystonia; Epilepsy; Mutation validation; Neurodegeneration; Phenotype-genotype relationship.
Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interest
E.A., T.L., F.M., P.F., C.S., J.F.C., S.D., L.J.O., and K.J.S. declare no competing interests. I.U.H. has performed research for Allergan, Boston Scientific, Great Lakes Neurotechnology, and Pfizer. His conflicts of interest are managed by Wake Forest School of Medicine. R.S-P. has support from the NIH (U01-NS094148), the Bigglesworth Family Foundation, and consults for Denali. S.B. has support from the Michael J. Fox Foundation and consults for Denali. A.B. performs research funded by NINDS, Revance, and Ipsen, and consults for Revance and Ipsen. Her conflicts of interest are managed by Wake Forest School of Medicine.
Figures


References
-
- Benarroch EE, 2011. Na+,K+-ATPase: Functions in the nervous system and involvement in neurologic disease. Neurology 76, 287–293. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

