Novel derivatives of anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitors: Synthesis, radiolabeling, and preliminary biological studies of fluoroethyl analogues of crizotinib, alectinib, and ceritinib
- PMID: 31425908
- PMCID: PMC7193943
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111571
Novel derivatives of anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitors: Synthesis, radiolabeling, and preliminary biological studies of fluoroethyl analogues of crizotinib, alectinib, and ceritinib
Abstract
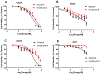
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK), an oncogenic receptor tyrosine kinase, is a therapeutic target in various cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer. Although several ALK inhibitors, including crizotinib, ceritinib, and alectinib, are approved for cancer treatment, their long-term benefit is often limited by the cancer's acquisition of resistance owing to secondary point mutations in ALK. Importantly, some ALK inhibitors cannot cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and thus have little or no efficacy against brain metastases. The introduction of a lipophilic moiety, such as a fluoroethyl group may improve the drug's BBB penetration. Herein, we report the synthesis of fluoroethyl analogues of crizotinib 1, alectinib 4, and ceritinib 9, and their radiolabeling with 18F for pharmacokinetic studies. The fluoroethyl derivatives and their radioactive analogues were obtained in good yields with high purity and good molar activity. A cytotoxicity screen in ALK-expressing H2228 lung cancer cells showed that the analogues had up to nanomolar potency and the addition of the fluorinated moiety had minimal impact overall on the potency of the original drugs. Positron emission tomography in healthy mice showed that the analogues had enhanced BBB penetration, suggesting that they have therapeutic potential against central nervous system metastases.
Keywords: Anaplastic lymphoma kinase; Brain metastasis; Lung cancer; PET; Targeted therapeutics.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
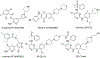

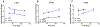






Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis and biological evaluations of 2-amino-4-(1-piperidine) pyridine derivatives as novel anti crizotinib-resistant ALK/ROS1 dual inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 Oct 1;179:358-375. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.06.043. Epub 2019 Jun 25. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31260890
-
The ALK inhibitors, alectinib and ceritinib, induce ALK-independent and STAT3-dependent glioblastoma cell death.Cancer Sci. 2021 Jun;112(6):2442-2453. doi: 10.1111/cas.14885. Epub 2021 May 1. Cancer Sci. 2021. PMID: 33728771 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Inhibitors in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2019 Apr;58(4):403-420. doi: 10.1007/s40262-018-0689-7. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2019. PMID: 29915924 Review.
-
Efficacy and Safety of ALK Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Elderly Patients with Advanced ALK-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Findings from the Real-Life Cohort.Oncol Res Treat. 2019;42(5):275-282. doi: 10.1159/000499086. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Oncol Res Treat. 2019. PMID: 30955009
-
Background and rationale of the eXalt3 trial investigating X-396 in the treatment of ALK+ non-small-cell lung cancer.Future Oncol. 2018 Aug;14(18):1781-1787. doi: 10.2217/fon-2017-0619. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Future Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29506392 Review.
Cited by
-
Piperidine: A Versatile Heterocyclic Ring for Developing Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors.ACS Omega. 2023 Oct 3;8(41):37731-37751. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c05883. eCollection 2023 Oct 17. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37867639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Piperidine Derivatives: Recent Advances in Synthesis and Pharmacological Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 2;24(3):2937. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032937. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Concomitant mutation status of ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancers and its prognostic impact on patients treated with crizotinib.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021 Mar;10(3):1525-1535. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-21-160. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33889527 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in drug delivery and targeting to the brain.J Control Release. 2022 Oct;350:668-687. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.08.051. Epub 2022 Sep 7. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 36057395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N-[18F]-Fluoroacetylcrizotinib: A potentially potent and selective PET tracer for molecular imaging of non-small cell lung cancer.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2020 Aug 15;30(16):127257. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2020.127257. Epub 2020 Jun 2. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2020. PMID: 32631505 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, Takada S, Yamashita Y, Ishikawa S, Fujiwara S, Watanabe H, Kurashina K, Hatanaka H, Bando M, Ohno S, Ishikawa Y, Aburatani H, Niki T, Sohara Y, Sugiyama Y, Mano H, Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer, Nature, 448 (2007) 561–566. 10.1038/nature05945 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cui JJ, Tran-Dubé M, Shen H, Nambu M, Kung PP, Pairish M, Jia L, Meng J, Funk L, Botrous I, McTigue M, Grodsky N, Ryan K, Padrique E, Alton G, Timofeevski S, Yamazaki S, Li Q, Zou H, Christensen J, Mroczkowski B, Bender S, Kania RS, Edwards MP, Structure based drug design of Crizotinib (PF-02341066), a potent and selective dual inhibitor of Mesenchymal-Epithelial Transition Factor (c-MET) Kinase and Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK), J Med Chem, 54 (2011) 6342–6363. 10.1021/jm2007613 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

