Novel derivatives of anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitors: Synthesis, radiolabeling, and preliminary biological studies of fluoroethyl analogues of crizotinib, alectinib, and ceritinib
- PMID: 31425908
- PMCID: PMC7193943
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111571
Novel derivatives of anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitors: Synthesis, radiolabeling, and preliminary biological studies of fluoroethyl analogues of crizotinib, alectinib, and ceritinib
Abstract
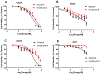
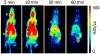
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK), an oncogenic receptor tyrosine kinase, is a therapeutic target in various cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer. Although several ALK inhibitors, including crizotinib, ceritinib, and alectinib, are approved for cancer treatment, their long-term benefit is often limited by the cancer's acquisition of resistance owing to secondary point mutations in ALK. Importantly, some ALK inhibitors cannot cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and thus have little or no efficacy against brain metastases. The introduction of a lipophilic moiety, such as a fluoroethyl group may improve the drug's BBB penetration. Herein, we report the synthesis of fluoroethyl analogues of crizotinib 1, alectinib 4, and ceritinib 9, and their radiolabeling with 18F for pharmacokinetic studies. The fluoroethyl derivatives and their radioactive analogues were obtained in good yields with high purity and good molar activity. A cytotoxicity screen in ALK-expressing H2228 lung cancer cells showed that the analogues had up to nanomolar potency and the addition of the fluorinated moiety had minimal impact overall on the potency of the original drugs. Positron emission tomography in healthy mice showed that the analogues had enhanced BBB penetration, suggesting that they have therapeutic potential against central nervous system metastases.
Keywords: Anaplastic lymphoma kinase; Brain metastasis; Lung cancer; PET; Targeted therapeutics.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
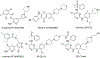

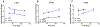






References
-
- Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, Takada S, Yamashita Y, Ishikawa S, Fujiwara S, Watanabe H, Kurashina K, Hatanaka H, Bando M, Ohno S, Ishikawa Y, Aburatani H, Niki T, Sohara Y, Sugiyama Y, Mano H, Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer, Nature, 448 (2007) 561–566. 10.1038/nature05945 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cui JJ, Tran-Dubé M, Shen H, Nambu M, Kung PP, Pairish M, Jia L, Meng J, Funk L, Botrous I, McTigue M, Grodsky N, Ryan K, Padrique E, Alton G, Timofeevski S, Yamazaki S, Li Q, Zou H, Christensen J, Mroczkowski B, Bender S, Kania RS, Edwards MP, Structure based drug design of Crizotinib (PF-02341066), a potent and selective dual inhibitor of Mesenchymal-Epithelial Transition Factor (c-MET) Kinase and Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK), J Med Chem, 54 (2011) 6342–6363. 10.1021/jm2007613 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

