A20 at the Crossroads of Cell Death, Inflammation, and Autoimmunity
- PMID: 31427375
- PMCID: PMC6942121
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a036418
A20 at the Crossroads of Cell Death, Inflammation, and Autoimmunity
Abstract
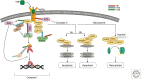
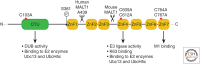
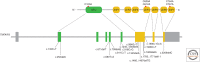
A20 is a potent anti-inflammatory protein, acting by inhibiting nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) signaling and inflammatory gene expression and/or by preventing cell death. Mutations in the A20/TNFAIP3 gene have been associated with a plethora of inflammatory and autoimmune pathologies in humans and in mice. Although the anti-inflammatory role of A20 is well accepted, fundamental mechanistic questions regarding its mode of action remain unclear. Here, we review new findings that further clarify the molecular and cellular mechanisms by which A20 controls inflammatory signaling and cell death, and discuss new evidence for its involvement in inflammatory and autoimmune disease development.
Copyright © 2020 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Aeschlimann FA, Batu ED, Canna SW, Go E, Gül A, Hoffmann P, Leavis HL, Ozen S, Schwartz DM, Stone DL, et al. 2018. A20 haploinsufficiency (HA20): Clinical phenotypes and disease course of patients with a newly recognised NF-κB-mediated autoinflammatory disease. Ann Rheum Dis 77: 728–735. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212403 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
