Biomineralization by particle attachment in early animals
- PMID: 31427519
- PMCID: PMC6731633
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1902273116
Biomineralization by particle attachment in early animals
Abstract
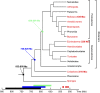
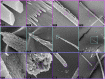
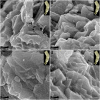
Crystallization by particle attachment (CPA) of amorphous precursors has been demonstrated in modern biomineralized skeletons across a broad phylogenetic range of animals. Precisely the same precursors, hydrated (ACC-H2O) and anhydrous calcium carbonate (ACC), have been observed spectromicroscopically in echinoderms, mollusks, and cnidarians, phyla drawn from the 3 major clades of eumetazoans. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) here also shows evidence of CPA in tunicate chordates. This is surprising, as species in these clades have no common ancestor that formed a mineralized skeleton and appear to have evolved carbonate biomineralization independently millions of years after their late Neoproterozoic divergence. Here we correlate the occurrence of CPA from ACC precursor particles with nanoparticulate fabric and then use the latter to investigate the antiquity of the former. SEM images of early biominerals from Ediacaran and Cambrian shelly fossils show that these early calcifiers used attachment of ACC particles to form their biominerals. The convergent evolution of biomineral CPA may have been dictated by the same thermodynamics and kinetics as we observe today.
Keywords: biomineralization; calcium carbonate; particle attachment; skeleton.
Copyright © 2019 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: P.U.P.A.G., C.-Y.S., and Tali Mass are coauthors on 2 research articles published in 2017.
Figures



References
-
- De Yoreo J. J., et al. , Crystallization by particle attachment in synthetic, biogenic, and geologic environments. Science 349, aaa6760 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Penn R. L., Banfield J. F., Oriented attachment and growth, twinning, polytypism, and formation of metastable phases: Insights from nanocrystalline TiO2. Am. Mineral. 83, 1077–1082 (1998).
-
- Banfield J. F., Welch S. A., Zhang H., Ebert T. T., Penn R. L., Aggregation-based crystal growth and microstructure development in natural iron oxyhydroxide biomineralization products. Science 289, 751–754 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Niederberger M., Cölfen H., Oriented attachment and mesocrystals: Non-classical crystallization mechanisms based on nanoparticle assembly. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 8, 3271–3287 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Killian C. E., et al. , Mechanism of calcite co-orientation in the sea urchin tooth. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 18404–18409 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

