Parkinson's disease is a type of amyloidosis featuring accumulation of amyloid fibrils of α-synuclein
- PMID: 31427526
- PMCID: PMC6731630
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1906124116
Parkinson's disease is a type of amyloidosis featuring accumulation of amyloid fibrils of α-synuclein
Abstract
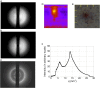
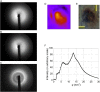
Many neurodegenerative diseases are characterized by the accumulation of abnormal protein aggregates in the brain. In Parkinson's disease (PD), α-synuclein (α-syn) forms such aggregates called Lewy bodies (LBs). Recently, it has been reported that aggregates of α-syn with a cross-β structure are capable of propagating within the brain in a prionlike manner. However, the presence of cross-β sheet-rich aggregates in LBs has not been experimentally demonstrated so far. Here, we examined LBs in thin sections of autopsy brains of patients with PD using microbeam X-ray diffraction (XRD) and found that some of them gave a diffraction pattern typical of a cross-β structure. This result confirms that LBs in the brain of PD patients contain amyloid fibrils with a cross-β structure and supports the validity of in vitro propagation experiments using artificially formed amyloid fibrils of α-syn. Notably, our finding supports the concept that PD is a type of amyloidosis, a disease featuring the accumulation of amyloid fibrils of α-syn.
Keywords: Lewy body; Parkinson’s disease; X-ray diffraction; cross-β structure.
Copyright © 2019 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Iwatsubo T., et al. , Visualization of A β 42(43) and A β 40 in senile plaques with end-specific A β monoclonals: Evidence that an initially deposited species is A β 42(43). Neuron 13, 45–53 (1994). - PubMed
-
- Papp M. I., Lantos P. L., The distribution of oligodendroglial inclusions in multiple system atrophy and its relevance to clinical symptomatology. Brain 117, 235–243 (1994). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

