Stress resilience is promoted by a Zfp189-driven transcriptional network in prefrontal cortex
- PMID: 31427770
- PMCID: PMC6713580
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-019-0462-8
Stress resilience is promoted by a Zfp189-driven transcriptional network in prefrontal cortex
Abstract
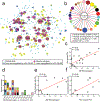
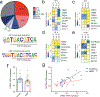
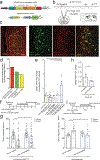
Understanding the transcriptional changes that are engaged in stress resilience may reveal novel antidepressant targets. Here we use gene co-expression analysis of RNA-sequencing data from brains of resilient mice to identify a gene network that is unique to resilience. Zfp189, which encodes a previously unstudied zinc finger protein, is the highest-ranked key driver gene in the network, and overexpression of Zfp189 in prefrontal cortical neurons preferentially activates this network and promotes behavioral resilience. The transcription factor CREB is a predicted upstream regulator of this network and binds to the Zfp189 promoter. To probe CREB-Zfp189 interactions, we employ CRISPR-mediated locus-specific transcriptional reprogramming to direct CREB or G9a (a repressive histone methyltransferase) to the Zfp189 promoter in prefrontal cortex neurons. Induction of Zfp189 with site-specific CREB is pro-resilient, whereas suppressing Zfp189 expression with G9a increases susceptibility. These findings reveal an essential role for Zfp189 and CREB-Zfp189 interactions in mediating a central transcriptional network of resilience.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests Statement
All authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


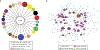
Comment in
-
Resilient networking.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2019 Nov;20(11):646-647. doi: 10.1038/s41583-019-0219-0. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31511656 No abstract available.
References
Methods-only references
-
- Neve RL, Neve KA, Nestler EJ & Carlezon WAJ Use of herpes virus amplicon vectors to study brain disorders. Biotechniques 39, 381–391 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- F30 MH110073/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA007359/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K99 DA045795/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DA007359/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH096678/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DA047233/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG057440/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG046170/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG057907/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH116900/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH096890/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH051399/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007280/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R00 DA045795/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

