The prevalence of childhood trauma in psychiatric outpatients
- PMID: 31428182
- PMCID: PMC6694480
- DOI: 10.1186/s12991-019-0239-1
The prevalence of childhood trauma in psychiatric outpatients
Abstract
Background: The aim of this present study was to compare the prevalence and type of trauma experienced by community sample with the outpatient sample with mental disorders.
Methods: A total of 354 outpatients, aged 14-35 years old, with mood disorders, schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders, adjustment disorder and anxiety disorder were recruited from a tertiary psychiatric hospital. A total of 100 healthy controls were recruited from the Singapore general population by snowballing. The Childhood Trauma Questionnaire-Short Form (CTQ-SF) designed to measure childhood trauma and the severity (e.g., physical abuse, emotional abuse, sexual abuse, physical neglect and emotional neglect) was administered to participants. Socio-demographic and clinical characteristics were obtained from interviews with the participants and from outpatients' medical records, respectively. Independent sample t tests and Chi-square tests were used to investigate the differences between the outpatient and community samples.
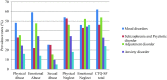
Results: Overall the CTQ-SF total and domain scores indicated that outpatient sample experienced higher rate of traumatic life events in childhood than community sample. Two most reported trauma types were emotional abuse (n = 81, 59.1%) and physical neglect (n = 74, 54%) reported by the mood disorder group. In the community sample, emotional neglect (n = 46, 46%) and physical neglect (n = 18, 18%) were the most commonly reported trauma type. Overall outpatient sample (n = 80, 22.6%) and community sample (n = 28, 28%) reported at least one type of trauma.
Conclusion: The findings indicate higher rates of CTQ-SF total and domain scores in outpatient sample demonstrating a higher rate of traumatic life events in childhood compared to community sample. Further research in childhood trauma is needed to improve the knowledge in psychiatric clinic practices.
Keywords: CTQ; Mood disorder; Outpatients; Prevalence; Psychotic disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Hughes K, Bellis MA, Hardcastle KA, Sethi D, Butchart A, Mikton C, et al. The effect of multiple adverse childhood experiences on health: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Public Health. 2017;2(8):e356–e366. - PubMed
-
- Bellis MA, Hughes K, Hardcastle K, Ashton K, Ford K, Quigg Z, et al. The impact of adverse childhood experiences on health service use across the life course using a retrospective cohort study. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2017;22(3):168–177.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources