Development of Zinc-Specific iCEST MRI as an Imaging Biomarker for Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 31430007
- PMCID: PMC7261412
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.201909429
Development of Zinc-Specific iCEST MRI as an Imaging Biomarker for Prostate Cancer
Abstract
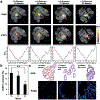
The healthy prostate contains the highest concentration of mobile zinc in the body. As this level decreases dramatically during the initial development of prostate cancer, in vivo detection of prostate zinc content may be applied for diagnosis of prostate cancer. Using 19 F ion chemical exchange saturation transfer magnetic resonance imaging (iCEST MRI) and TF-BAPTA as a fluorinated Zn-binding probe with micromolar sensitivity, we show that iCEST MRI is able to differentiate between normal and malignant prostate cells with a 10-fold difference in contrast following glucose-stimulated zinc secretion in vitro. The iCEST signal decreased in normal prostate cells upon downregulation of the ZIP1 zinc transporter. In vivo, using an orthotopic prostate cancer mouse model and a transgenic adenocarcinoma of the mouse prostate (TRAMP) model, a gradual decrease of >300 % in iCEST contrast following the transition of normal prostate epithelial cells to cancer cells was detected.
Keywords: MRI; imaging agents; prostate cancer; zinc.
© 2019 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

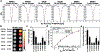



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

