Facile Formation of Anatase/Rutile TiO2 Nanocomposites with Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity
- PMID: 31430852
- PMCID: PMC6719911
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24162996
Facile Formation of Anatase/Rutile TiO2 Nanocomposites with Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity
Abstract
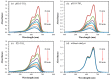
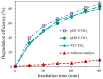
Anatase/rutile mixed-phase TiO2 nanoparticles were synthesized through a simple sol-gel route with further calcination using inexpensive titanium tetrachloride as a titanium source, which effectively reduces the production cost. The structural and optical properties of the prepared materials were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and UV-vis adsorption. The specific surface area was also analyzed by Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) method. The anatase/rutile mixed-phase TiO2 nanocomposites containing of rod-like, cuboid, and some irregularly shaped anatase nanoparticles (exposed {101} facets) with sizes ranging from tens to more than 100 nanometers, and rod-like rutile nanoparticles (exposed {110} facets) with sizes ranging from tens to more than 100 nanometers. The photocatalytic activities of the obtained anatase/rutile mixed-phase TiO2 nanoparticles were investigated and compared by evaluating the degradation of hazardous dye methylene blue (MB) under ultraviolet light illumination. Compared to the commercial Degussa P25-TiO2, the mixed-phase TiO2 nanocomposites show better photocatalytic activity, which can be attributed to the optimal anatase to rutile ratio and the specific exposed crystal surface on the surface. The anatase/rutile TiO2 nanocomposites obtained at pH 1.0 (pH1.0-TiO2) show the best photocatalytic activity, which can be attributed to the optimal heterojunction structure, the smaller average particle size, and the presence of a specific exposed crystal surface. The enhanced photocatalytic activity makes the prepared anatase/rutile TiO2 photocatalysts a potential candidate in the removal of the organic dyes from colored wastewater.
Keywords: anatase/rutile nanocomposites; photocatalytic activity; {101} facets; {110} facets.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Liu X., Li Y., Deng D., Chen N., Xing X., Wang Y. A one-step nonaqueous sol–gel route to mixed-phase TiO2 with enhanced photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B under visible light. CrystEngComm. 2016;18:1964–1975. doi: 10.1039/C5CE02322J. - DOI
-
- Konstantinou I.K., Albanis T.A. TiO2-assisted photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes in aqueous solution: Kinetic and mechanistic investigations: A review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2004;49:1–14. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2003.11.010. - DOI
-
- Han B., Chen Z., Louhi-Kultanen M. Effect of a pulsed electric field on the synthesis of TiO2 and its photocatalytic performance under visible light irradiation. Powder Technol. 2017;307:137–144. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2016.11.053. - DOI
-
- Tang R., Yin L. Enhanced photovoltaic performance of dye-sensitized solar cells based on Sr-doped TiO2/SrTiO3 nanorod array heterostructures. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2015;3:17417–17425. doi: 10.1039/C5TA03810C. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

