Laparoscopic Hiatal Hernia Repair Followed by Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication With EsophyX Device (HH + TIF): Efficacy and Safety in Two Community Hospitals
- PMID: 31431138
- PMCID: PMC6843624
- DOI: 10.1177/1553350619869449
Laparoscopic Hiatal Hernia Repair Followed by Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication With EsophyX Device (HH + TIF): Efficacy and Safety in Two Community Hospitals
Abstract
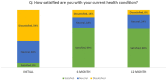
The TIF (transoral incisionless fundoplication) 2.0 procedure is indicated for patients with a hiatal hernia less than 2 cm. Many patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) require hiatal hernia repair. This study examined the safety and efficacy when repairing defects in 2 anatomical structures (hiatus and lower esophageal sphincter) in a concomitant set of procedures in patients with hiatal hernias between 2 and 5 cm. Methods. Prospective data were collected from 99 patients who underwent hiatal hernia repair followed immediately by the TIF procedure (HH + -TIF). GERD-HRQL (Health-Related Quality of Life), RSI (Reflux Symptom Index), and GERSS (Gastroesophageal Reflux Symptom Score) questionnaires were administered before the procedure and mailed at 6 and 12 months. Results. Ninety-nine patients were enrolled, and all were symptomatic on PPI medications with hiatal hernias between 2 and 5 cm. Overall baseline GERD-HRQL scores indicated daily bothersome symptoms. At 12-month follow-up, median GERD-HRQL scores improved by 17 points, indicating that subjects had no bothersome symptoms. The median GERSS scores decreased from 25.0 at baseline to 1.0 and 90% of subjects reported having effective symptom control (score <18) at 12 months. Seventy-seven percent of subjects reported effective control of laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) symptoms at 12 months with an RSI score of 13 or less. At 12 months, 74% of subjects reported that they were not using proton pump inhibitors. All measures were statistically improved at P < .05. There were no adverse effects reported. Conclusion. HH + TIF provides significant symptom control for heartburn and regurgitation with no long-term dysphagia or gas bloat normally associated with traditional antireflux procedures. Most patients reported durable symptom control and satisfaction with health condition at 12 months.
Keywords: TIF; esophageal surgery; evidence based medicine/surgery; flexible endoscopy; gastric surgery; hiatal hernia repair; interventional endoscopy; transoral incisionless fundoplication.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Kahrilas PJ, Shaheen NJ, Vaezi MF. American Gastroenterological Association Institute technical review on the management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:1392-1413. - PubMed
-
- Arj A, Razavi Zade M, Yavari M, Akbari H, Zamani B, Asemi Z. Proton pump inhibitors use and change in bone mineral density. Int J Rheum Dis. 2016;19:864-868. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

