Hypothesis: Role of Reduced Hepatic Insulin Clearance in the Pathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 31431441
- PMCID: PMC6702636
- DOI: 10.2337/db19-0098
Hypothesis: Role of Reduced Hepatic Insulin Clearance in the Pathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes
Erratum in
-
Erratum. Hypothesis: Role of Reduced Hepatic Insulin Clearance in the Pathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2019;68:1709-1716.Diabetes. 2019 Dec;68(12):2350. doi: 10.2337/db19-er12a. Epub 2019 Oct 9. Diabetes. 2019. PMID: 31597638 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
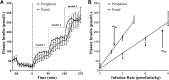
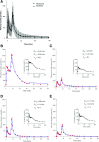
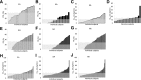
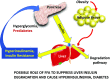
There is wide variance among individuals in the fraction of insulin cleared by the liver (20% to 80%). Hepatic insulin clearance is 67% lower in African Americans than European Americans. Clearance is also lower in African American children 7-13 years of age. Lower hepatic insulin clearance will result in peripheral hyperinsulinemia: this exacerbates insulin resistance, which stresses the β-cells, possibly resulting in their ultimate failure and onset of type 2 diabetes. We hypothesize that lower insulin clearance can be a primary cause of type 2 diabetes in at-risk individuals.
© 2019 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures

References
-
- Kahn CR. Banting Lecture. Insulin action, diabetogenes, and the cause of type II diabetes. Diabetes 1994;43:1066–1084 - PubMed
-
- Porte D Jr, Kahn SE. Mechanisms for hyperglycemia in type II diabetes mellitus: therapeutic implications for sulfonylurea treatment--an update. Am J Med 1991;90(6A):8S–14S - PubMed
-
- Weyer C, Hanson RL, Tataranni PA, Bogardus C, Pratley RE. A high fasting plasma insulin concentration predicts type 2 diabetes independent of insulin resistance: evidence for a pathogenic role of relative hyperinsulinemia. Diabetes 2000;49:2094–2101 - PubMed
-
- ter Horst KW, Gilijamse PW, Koopman KE, et al. . Insulin resistance in obesity can be reliably identified from fasting plasma insulin. Int J Obes 2015;39:1703–1709 - PubMed
-
- Brüning JC, Michael MD, Winnay JN, et al. . A muscle-specific insulin receptor knockout exhibits features of the metabolic syndrome of NIDDM without altering glucose tolerance. Mol Cell 1998;2:559–569 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

