Chemotherapy-Induced Metastasis: Molecular Mechanisms, Clinical Manifestations, Therapeutic Interventions
- PMID: 31431464
- PMCID: PMC6744993
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-1147
Chemotherapy-Induced Metastasis: Molecular Mechanisms, Clinical Manifestations, Therapeutic Interventions
Abstract
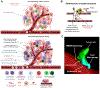
Chemotherapy offers long-term clinical benefits to many patients with advanced cancer. However, recent evidence has linked the cytotoxic effects of chemotherapy with the de novo elicitation of a prometastatic tumor microenvironment. This "modified" tumor microenvironment is triggered by a chemotherapy-driven cytokine storm or through direct effects of certain chemotherapeutics on stromal and/or immune cells, the most critical being tumor-associated macrophages. These chemotherapy-educated cells act as facilitators in tumor-host cell interactions promoting the establishment of distant metastasis. Certain clinical studies now offer substantial evidence that prometastatic changes are indeed identified in the tumor microenvironment of certain patient subpopulations, especially those that do not present with any pathologic response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Deciphering the exact contextual prerequisites for chemotherapy-driven metastasis will be paramount for designing novel mechanism-based treatments for circumventing chemotherapy-induced metastasis.
©2019 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest:
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diverse macrophages polarization in tumor microenvironment.Arch Pharm Res. 2016 Nov;39(11):1588-1596. doi: 10.1007/s12272-016-0820-y. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Arch Pharm Res. 2016. PMID: 27562774 Review.
-
Heparanase: From basic research to therapeutic applications in cancer and inflammation.Drug Resist Updat. 2016 Nov;29:54-75. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2016.10.001. Epub 2016 Oct 6. Drug Resist Updat. 2016. PMID: 27912844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemotherapy-induced metastasis: mechanisms and translational opportunities.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2018 Apr;35(4):269-284. doi: 10.1007/s10585-017-9870-x. Epub 2018 Jan 6. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2018. PMID: 29307118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of host response to chemotherapy: resistance, metastasis and clinical implications.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2024 Aug;41(4):495-507. doi: 10.1007/s10585-023-10243-5. Epub 2023 Nov 24. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2024. PMID: 37999904 Review.
-
Chemotherapy acts as an adjuvant to convert the tumor microenvironment into a highly permissive state for vaccination-induced antitumor immunity.Cancer Res. 2013 Apr 15;73(8):2493-504. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4241. Epub 2013 Feb 15. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23418322 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Post-Radiotherapy Exosomal Non-Coding RNA and Hemograms for Early Death Prediction in Patients with Cervical Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 21;25(1):126. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010126. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203297 Free PMC article.
-
Individualized evaluation of risk and prognosis in uterine leiomyosarcoma patients with synchronous distant metastases: a real-world retrospective study.Front Oncol. 2024 Sep 25;14:1417226. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1417226. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39386189 Free PMC article.
-
Stress-Inducible Gene Atf3 Dictates a Dichotomous Macrophage Activity in Chemotherapy-Enhanced Lung Colonization.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 8;22(14):7356. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147356. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34298975 Free PMC article.
-
Hematogenous Dissemination of Breast Cancer Cells From Lymph Nodes Is Mediated by Tumor MicroEnvironment of Metastasis Doorways.Front Oncol. 2020 Oct 26;10:571100. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.571100. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33194666 Free PMC article.
-
Oncology during the New Coronavirus Infection Pandemic.Her Russ Acad Sci. 2022;92(4):456-463. doi: 10.1134/S1019331622040141. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Her Russ Acad Sci. 2022. PMID: 36091860 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

