A molecule inducing androgen receptor degradation and selectively targeting prostate cancer cells
- PMID: 31431473
- PMCID: PMC6703138
- DOI: 10.26508/lsa.201800213
A molecule inducing androgen receptor degradation and selectively targeting prostate cancer cells
Abstract
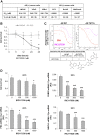
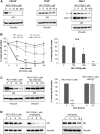
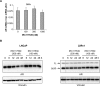
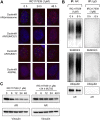
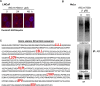
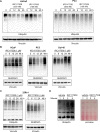
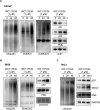
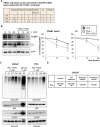
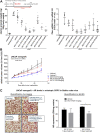
Aberrant androgen signaling drives prostate cancer and is targeted by drugs that diminish androgen production or impede androgen-androgen receptor (AR) interaction. Clinical resistance arises from AR overexpression or ligand-independent constitutive activation, suggesting that complete AR elimination could be a novel therapeutic strategy in prostate cancers. IRC117539 is a new molecule that targets AR for proteasomal degradation. Exposure to IRC117539 promotes AR sumoylation and ubiquitination, reminiscent of therapy-induced PML/RARA degradation in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Critically, ex vivo, IRC117539-mediated AR degradation induces prostate cancer cell viability loss by inhibiting AR signaling, even in androgen-insensitive cells. This approach may be beneficial for castration-resistant prostate cancer, which remains a clinical issue. In xenograft models, IRC117539 is as potent as enzalutamide in impeding growth, albeit less efficient than expected from ex vivo studies. Unexpectedly, IRC117539 also behaves as a weak proteasome inhibitor, likely explaining its suboptimal efficacy in vivo. Our studies highlight the feasibility of AR targeting for degradation and off-target effects' importance in modulating drug activity in vivo.
© 2019 Auvin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
S Auvin, G Mautino, F Meyer-Losic, and T Bashir are employees of IPSEN that also paid US salary. This study was funded by IPSEN.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Unique targeting of androgen-dependent and -independent AR signaling in prostate cancer to overcome androgen resistance.FASEB J. 2020 Sep;34(9):11511-11528. doi: 10.1096/fj.201903167R. Epub 2020 Jul 26. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 32713076
-
Discovery of ODM-201, a new-generation androgen receptor inhibitor targeting resistance mechanisms to androgen signaling-directed prostate cancer therapies.Sci Rep. 2015 Jul 3;5:12007. doi: 10.1038/srep12007. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26137992 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond androgen deprivation: ancillary integrative strategies for targeting the androgen receptor addiction of prostate cancer.Integr Cancer Ther. 2014 Sep;13(5):386-95. doi: 10.1177/1534735414534728. Epub 2014 May 26. Integr Cancer Ther. 2014. PMID: 24867960
-
Androgens in prostate cancer: A tale that never ends.Cancer Lett. 2021 Sep 28;516:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.04.010. Epub 2021 May 28. Cancer Lett. 2021. PMID: 34052327 Review.
-
Investigational therapies targeting the androgen signaling axis and the androgen receptor and in prostate cancer - recent developments and future directions.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2018 Oct;27(10):811-822. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2018.1513490. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2018. PMID: 30118330 Review.
Cited by
-
Sumoylation in Physiology, Pathology and Therapy.Cells. 2022 Feb 26;11(5):814. doi: 10.3390/cells11050814. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35269436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sumoylation of Cas9 at lysine 848 regulates protein stability and DNA binding.Life Sci Alliance. 2022 Jan 12;5(4):e202101078. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202101078. Print 2022 Apr. Life Sci Alliance. 2022. PMID: 35022246 Free PMC article.
-
The role of ubiquitination in spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Oct 6;15:1020143. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.1020143. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36277484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Visualization of the protein-protein interactions of hormone receptors in hormone-dependent cancer research.Endocr Oncol. 2022 Oct 3;2(1):R132-R142. doi: 10.1530/EO-22-0059. eCollection 2022 Jan. Endocr Oncol. 2022. PMID: 37435453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A new compound targets the AF-1 of androgen receptor and decreases its activity and protein levels in prostate cancer cells.Am J Cancer Res. 2020 Dec 1;10(12):4607-4623. eCollection 2020. Am J Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33415022 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ablain J, Nasr R, Bazarbachi A, de The H (2011) The drug-induced degradation of oncoproteins: An unexpected Achilles’ heel of cancer cells? Cancer Discov 1: 117–127. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11-0087 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
