Syringeable immunotherapeutic nanogel reshapes tumor microenvironment and prevents tumor metastasis and recurrence
- PMID: 31431623
- PMCID: PMC6702226
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-11730-8
Syringeable immunotherapeutic nanogel reshapes tumor microenvironment and prevents tumor metastasis and recurrence
Abstract
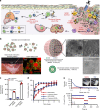
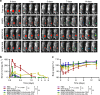
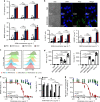
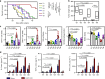
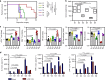
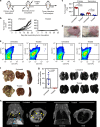
The low response rate of current cancer immunotherapy suggests the presence of few antigen-specific T cells and a high number of immunosuppressive factors in tumor microenvironment (TME). Here, we develop a syringeable immunomodulatory multidomain nanogel (iGel) that overcomes the limitation by reprogramming of the pro-tumoral TME to antitumoral immune niches. Local and extended release of immunomodulatory drugs from iGel deplete immunosuppressive cells, while inducing immunogenic cell death and increased immunogenicity. When iGel is applied as a local postsurgical treatment, both systemic antitumor immunity and a memory T cell response are generated, and the recurrence and metastasis of tumors to lungs and other organs are significantly inhibited. Reshaping of the TME using iGel also reverts non-responding groups to checkpoint blockade therapies into responding groups. The iGel is expected as an immunotherapeutic platform that can reshape immunosuppressive TMEs and synergize cancer immunotherapy with checkpoint therapies, with minimized systemic toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Modulation of the tumor microenvironment by intratumoral administration of IMO-2125, a novel TLR9 agonist, for cancer immunotherapy.Int J Oncol. 2018 Sep;53(3):1193-1203. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4456. Epub 2018 Jun 27. Int J Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29956749
-
Intratumoral CpG-B Promotes Antitumoral Neutrophil, cDC, and T-cell Cooperation without Reprograming Tolerogenic pDC.Cancer Res. 2018 Jun 15;78(12):3280-3292. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-2549. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29588348
-
A Designer Scaffold with Immune Nanoconverters for Reverting Immunosuppression and Enhancing Immune Checkpoint Blockade Therapy.Adv Mater. 2019 Oct;31(42):e1903242. doi: 10.1002/adma.201903242. Epub 2019 Sep 6. Adv Mater. 2019. PMID: 31490604
-
Nanoengineered Immune Niches for Reprogramming the Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment and Enhancing Cancer Immunotherapy.Adv Mater. 2019 Aug;31(34):e1803322. doi: 10.1002/adma.201803322. Epub 2019 Feb 18. Adv Mater. 2019. PMID: 30773696 Review.
-
Combinatory therapy adopting nanoparticle-based cancer vaccination with immune checkpoint blockade for treatment of post-surgical tumor recurrences.J Control Release. 2018 Sep 10;285:56-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.07.011. Epub 2018 Jul 6. J Control Release. 2018. PMID: 30008371 Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor extracellular matrix modulating strategies for enhanced antitumor therapy of nanomedicines.Mater Today Bio. 2022 Jul 15;16:100364. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100364. eCollection 2022 Dec. Mater Today Bio. 2022. PMID: 35875197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Injectable Epigenetic Autophagic Modulatory Hydrogel for Boosting Umbilical Cord Blood NK Cell Therapy Prevents Postsurgical Relapse of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022 Aug;9(23):e2201271. doi: 10.1002/advs.202201271. Epub 2022 Jun 16. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022. PMID: 35712750 Free PMC article.
-
Attachable Hydrogel Containing Indocyanine Green for Selective Photothermal Therapy against Melanoma.Biomolecules. 2020 Jul 29;10(8):1124. doi: 10.3390/biom10081124. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32751399 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered nanoparticles for precise targeted drug delivery and enhanced therapeutic efficacy in cancer immunotherapy.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Aug;14(8):3432-3456. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.05.010. Epub 2024 May 13. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 39220871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid-based nanoparticles for cancer immunotherapy.Med Rev (2021). 2023 Aug 17;3(3):230-269. doi: 10.1515/mr-2023-0020. eCollection 2023 Jun. Med Rev (2021). 2023. PMID: 37789955 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

