SWATH-MS screening strategy for the determination of food dyes in spices by UHPLC-HRMS
- PMID: 31432009
- PMCID: PMC6694849
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fochx.2019.100009
SWATH-MS screening strategy for the determination of food dyes in spices by UHPLC-HRMS
Abstract
A multi-class wide-scope screening method for the detection and identification of artificial colours and illegal dyes in spices was developed for regulatory purposes. The screening was carried out by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography hyphenated with a quadrupole/time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-QTOF-MS) with sequential window acquisition of all theoretical fragment-ion spectra (SWATH) and was validated with forty-one compounds by spiking experiments in curry and paprika extracts. In order to detect and identify the compounds with a high level of confidence, a home-made tandem mass spectrometry (QTOF-MS/MS) database of approximately one hundred illegal dyes and artificial colours was created. The procedure was then used to screen field samples of spices and spice blends purchased from Swiss markets. Sudan IV, Sudan I, bixin (E160b) and Ponceau 4R (E124) were all detected among the eight non-compliant samples.
Keywords: Artificial colours; Food dyes; QTOF; SWATH-MS; Spices; Sudan dyes.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
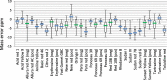
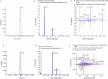
Similar articles
-
Applying 'Sequential Windowed Acquisition of All Theoretical Fragment Ion Mass Spectra' (SWATH) for systematic toxicological analysis with liquid chromatography-high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015 Jan;407(2):405-14. doi: 10.1007/s00216-014-8262-1. Epub 2014 Nov 1. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015. PMID: 25366975
-
Comprehensive MS/MS profiling by UHPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS using SWATH data-independent acquisition for the study of platelet lipidomes in coronary artery disease.Anal Chim Acta. 2019 Jan 10;1046:1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2018.08.060. Epub 2018 Sep 3. Anal Chim Acta. 2019. PMID: 30482286
-
Comparison of information-dependent acquisition, SWATH, and MS(All) techniques in metabolite identification study employing ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry.Anal Chem. 2014 Jan 21;86(2):1202-9. doi: 10.1021/ac403385y. Epub 2014 Jan 2. Anal Chem. 2014. PMID: 24383719
-
Screening of synthetic PDE-5 inhibitors and their analogues as adulterants: analytical techniques and challenges.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014 Jan;87:176-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.04.037. Epub 2013 May 6. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014. PMID: 23721687 Review.
-
The use of sequential window acquisition of all theoretical fragment ion spectra (SWATH), a data-independent acquisition high-resolution mass spectrometry approach, in forensic toxicological regimes: A review.Drug Test Anal. 2025 Feb;17(2):300-310. doi: 10.1002/dta.3700. Epub 2024 May 9. Drug Test Anal. 2025. PMID: 38724180 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction Based on Magnetic Sulfonated Reduced Graphene Oxide for HPLC-MS/MS Analysis of Illegal Basic Dyes in Foods.Molecules. 2021 Dec 7;26(24):7427. doi: 10.3390/molecules26247427. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34946507 Free PMC article.
-
A simple method to quantify azo dyes in spices based on flow injection chromatography combined with chemometric tools.J Food Sci Technol. 2022 Jul;59(7):2764-2775. doi: 10.1007/s13197-021-05299-8. Epub 2021 Oct 27. J Food Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 35734112 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in electrochemical detection of common azo dyes.Forensic Toxicol. 2025 Jan;43(1):1-21. doi: 10.1007/s11419-024-00696-y. Epub 2024 Aug 2. Forensic Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39093537 Review.
-
Analytical and Sample Preparation Techniques for the Determination of Food Colorants in Food Matrices.Foods. 2020 Jan 7;9(1):58. doi: 10.3390/foods9010058. Foods. 2020. PMID: 31936025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Voltammetric Sensor Based on the Combination of Tin and Cerium Dioxide Nanoparticles with Surfactants for Quantification of Sunset Yellow FCF.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Jan 31;24(3):930. doi: 10.3390/s24030930. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38339646 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Commission Decision 2002/657/EC, implementing Council Directive 96/23/EC concerning the performance of analytical methods and the interpretation of results. (2002). Official Journal of European Communities, L221, 8–36.
-
- Amchova P., Kotolova H., Ruda-Kucerova J. Health safety issues of synthetic food colorants. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology. 2015;73(3):914–922. - PubMed
-
- Ates E., Mittendorf K., Senyuva H. LC/MS method using cloud point extraction for the determination of permitted and illegal food colors in liquid, semiliquid, and solid food matrixes: Single-laboratory validation. Journal of AOAC International. 2011;94(6):1853–1862. - PubMed
-
- Botek P., Poustka J., Hajšlová J. Determination of banned dyes in spices by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Czech Journal of Food Sciences. 2007;25(1):17–24.
-
- CH/817.022.31. (2017). Ordonnance du DFI sur les additifs admis dans les denrées alimentaires. In OSAV (Ed.), vol. 817.022.31: Département Fédéral de l'Intérieur.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

