Myocardial Viability and Long-Term Outcomes in Ischemic Cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 31433921
- PMCID: PMC6814246
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1807365
Myocardial Viability and Long-Term Outcomes in Ischemic Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
Background: The role of assessment of myocardial viability in identifying patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy who might benefit from surgical revascularization remains controversial. Furthermore, although improvement in left ventricular function is one of the goals of revascularization, its relationship to subsequent outcomes is unclear.
Methods: Among 601 patients who had coronary artery disease that was amenable to coronary-artery bypass grafting (CABG) and who had a left ventricular ejection fraction of 35% or lower, we prospectively assessed myocardial viability using single-photon-emission computed tomography, dobutamine echocardiography, or both. Patients were randomly assigned to undergo CABG and receive medical therapy or to receive medical therapy alone. Left ventricular ejection fraction was measured at baseline and after 4 months of follow-up in 318 patients. The primary end point was death from any cause. The median duration of follow-up was 10.4 years.
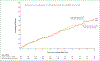
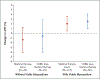
Results: CABG plus medical therapy was associated with a lower incidence of death from any cause than medical therapy alone (182 deaths among 298 patients in the CABG group vs. 209 deaths among 303 patients in the medical-therapy group; adjusted hazard ratio, 0.73; 95% confidence interval, 0.60 to 0.90). However, no significant interaction was observed between the presence or absence of myocardial viability and the beneficial effect of CABG plus medical therapy over medical therapy alone (P = 0.34 for interaction). An increase in left ventricular ejection fraction was observed only among patients with myocardial viability, irrespective of treatment assignment. There was no association between changes in left ventricular ejection fraction and subsequent death.
Conclusions: The findings of this study do not support the concept that myocardial viability is associated with a long-term benefit of CABG in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy. The presence of viable myocardium was associated with improvement in left ventricular systolic function, irrespective of treatment, but such improvement was not related to long-term survival. (Funded by the National Institutes of Health; STICH ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT00023595.).
Copyright © 2019 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures

Comment in
-
Myocardial Viability and Long-Term Outcomes in Ischemic Cardiomyopathy.N Engl J Med. 2019 Dec 12;381(24):2373. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1913972. N Engl J Med. 2019. PMID: 31826350 No abstract available.
-
Myocardial Viability and Long-Term Outcomes in Ischemic Cardiomyopathy.N Engl J Med. 2019 Dec 12;381(24):2373. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1913972. N Engl J Med. 2019. PMID: 31826351 No abstract available.
References
-
- Felker GM, Shaw LK, O’Connor CM. A standardized definition of ischemic cardiomyopathy for use in clinical research. J Am Coll Cardiol 2002;39:210–8. - PubMed
-
- Gheorghiade M, Sopko G, De Luca L, et al. Navigating the crossroads of coronary artery disease and heart failure. Circulation 2006;114:1202–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
- HL-069011/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL070011/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL069013/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-069010/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL069012/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-070011/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-069015/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01-HL-069009/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105853/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070011/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL069010/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL105853/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-069012/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL069009/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-069013/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL072683/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL069015/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL069011/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-072683/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
