Comparison of Phenolic Compounds and the Antioxidant Activities of Fifteen Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat cv. 'Hangbaiju' in China
- PMID: 31434279
- PMCID: PMC6720787
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox8080325
Comparison of Phenolic Compounds and the Antioxidant Activities of Fifteen Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat cv. 'Hangbaiju' in China
Abstract
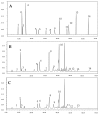
This study investigated the phenolic compounds of 15 Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat cv. 'Hangbaiju', including 6 'Duoju' and 9 'Taiju', using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The antioxidant activities of these 'Hangbaiju' were estimated by DPPH, ABTS and FRAP assays. Results show that a total of 14 phenolic compounds were detected in these flowers, including 3 mono-caffeoylquinic acids, 3 di-caffeoylquinic acids, 1 phenolic acid and 7 flavonoids. 'Duoju' and 'Taiju' possess different concentrations of phenolic compounds, and 'Taiju' exhibits higher caffeoylquinic acids and stronger antioxidant activities than 'Duoju'. Caffeoylquinic acids show a strong correlation with the antioxidant activities of the samples. Principal component analysis (PCA) reveals an obvious separation between 'Duoju' and 'Taiju', using phenolic compounds as variables. Apigenin-7-O-glucoside, 3,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid, luteolin and acacetin were found to be the key phenolic compounds to differentiate 'Duoju' from 'Taiju'.
Keywords: HPLC; antioxidant capacity; chrysanthemum; phenolic compounds; principal component analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chen L., Kotani A., Kusu F., Wang Z., Zhu J., Hakamata H. Quantitative comparison of caffeoylquinic acids and flavonoids in Chrysanthemum morifolium flowers and their sulfur-fumigated products by three-channel liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2015;63:25–32. doi: 10.1248/cpb.c14-00515. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Qu L., Ruan J.Y., Jin L.J., Shi W.Z., Li X.X., Han L.F., Zhang Y., Wang T. Xanthine oxidase inhibitory effects of the constituents of Chrysanthemum morifolium stems. Phytochem. Lett. 2017;19:39–45. doi: 10.1016/j.phytol.2016.11.007. - DOI
-
- Ma D., Wako Y. Evaluation of phenolic compounds and neurotrophic/neuroprotective activity of cultivar extracts derived from Chrysanthemum morifolium flowers. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2017;23:457–467. doi: 10.3136/fstr.23.457. - DOI
-
- Lin L.Z., Harnly J.M. Identification of the phenolic components of chrysanthemum flower (Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat.) Food Chem. 2010;120:319–326. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.09.083. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 31871763/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 20182008/Open Foundation of Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Food Nutrition and Human Health
- LQ18C200002 and LQ18C200003/Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province
- 2018R415014/Students Science and Technology Innovation Activity Plan of Zhejiang Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

