Current outlook on radionuclide delivery systems: from design consideration to translation into clinics
- PMID: 31434562
- PMCID: PMC6704557
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-019-0524-9
Current outlook on radionuclide delivery systems: from design consideration to translation into clinics
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Current outlook on radionuclide delivery systems: from design consideration to translation into clinics.J Nanobiotechnology. 2020 Jan 2;18(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12951-019-0558-z. J Nanobiotechnology. 2020. PMID: 31898505 Free PMC article.
Abstract
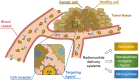
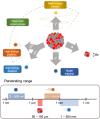
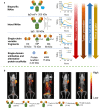
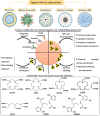
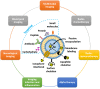
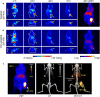
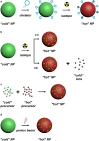
Radiopharmaceuticals have proven to be effective agents, since they can be successfully applied for both diagnostics and therapy. Effective application of relevant radionuclides in pre-clinical and clinical studies depends on the choice of a sufficient delivery platform. Herein, we provide a comprehensive review on the most relevant aspects in radionuclide delivery using the most employed carrier systems, including, (i) monoclonal antibodies and their fragments, (ii) organic and (iii) inorganic nanoparticles, and (iv) microspheres. This review offers an extensive analysis of radionuclide delivery systems, the approaches of their modification and radiolabeling strategies with the further prospects of their implementation in multimodal imaging and disease curing. Finally, the comparative outlook on the carriers and radionuclide choice, as well as on the targeting efficiency of the developed systems is discussed.
Keywords: Diagnostic and therapeutic radionuclides; Drug carrier systems; Microspheres; Monoclonal antibodies; Multimodal imaging; Nanoparticles; Nuclear medicine; Radiopharmaceuticals; Theranostics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Srivastava SC, Mausner LF. Therapeutic radionuclides: production, physical characteristics, and applications. In: Baum RP, editor. Therapeutic nuclear medicine. Berlin: Springer; 2014. pp. 11–50.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

