Effectiveness of the team-based learning (TBL) strategy on medical students' performance
- PMID: 31435305
- PMCID: PMC6695008
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtumed.2017.09.003
Effectiveness of the team-based learning (TBL) strategy on medical students' performance
Abstract
Objectives: Team-based learning (TBL) represents a new and interesting educational strategy. It helps to enhance students' professional competencies and ideally works to prepare them in their pursuit of lifelong learning. The aim of this study is to evaluate the effectiveness of TBL as an educational strategy on medical students' performance in a problem-based learning (PBL) curriculum.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted through a self-designed questionnaire. It was constructed to examine several aspects of TBL, including cognition, social skills, high school educational system, and personal development. A total of 112 students were invited to participate in the study and 100 completed the survey. Individual-readiness assurance test (IRAT) and group-readiness assurance test (GRAT) scores were collected and the data were analysed and compared to the results of the final assessment using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS).
Results: A total of 52 students (52%) described TBL as fostering a cooperative learning environment and 64 students (64%) found the materials to be easier to understand when discussed among themselves as a group. Compared to final examination results, there was a significant correlation (p = 0.0001) between IRAT performance and final exam score. In addition, there was a significant correlation between high school education system and IRAT score, where the best performance was observed among students coming from schools using the British curriculum.
Conclusions: The overall perception and attitude of students toward the TBL system was positive and promising. Nevertheless, there are some notes and areas of concern that must be re-examined and remedied to improve TBL as an educational tool.
أهداف البحث: يمثل 'التعلم المبني على فريق' استراتيجية تعليمية جديدة ومثيرة للاهتمام. فهو يساعد على تعزيز الكفاءات المهنية للطلاب، ويعمل بشكل مثالي لإعدادهم في سعيهم للتعلم مدى الحياة. الهدف من هذه الدراسة هو تقييم فاعلية 'التعلم المبني على فريق' كاستراتيجية تعليمية، على أداء طلاب طب يدرسون في منهج تعلم مبني على مشكلة.
طرق البحث: أجريت دراسة مقطعية من خلال استبانة ذاتية التصميم. شُيّد الاستبانة لفحص عدة جوانب من 'التعلم المبني على فريق'، بما في ذلك الإدراك، والمهارات الاجتماعية، ونظام التعليم في المدرسة الثانوية، والتنمية الذاتية. تمت دعوة ١١٢ طالبا للمشاركة في الدراسة وأكمل ١٠٠ منهم الاستبانة. تم جمع نتائج كل من 'اختبارات ضمان استعداد الفرد' و'اختبارات ضمان استعداد المجموعة' كما تم تحليل البيانات ومقارنتها بنتائج التقييم النهائي باستخدام البرنامج الإحصائي للعلوم الاجتماعية.
النتائج: وصف ٥٢ طالبا (٥٢٪) 'التعلم المبني على فريق' بأنه يتبنى بيئة تعلم تعاونية ووجد ٦٤ طالبا (٦٤٪) أن المواد أسهل فهما عند مناقشتها فيما بينهم كمجموعة. وبالمقارنة مع نتائج الامتحانات النهائية، كان هناك ارتباط ذا قيمة إحصائية بين أداء 'اختبارات ضمان استعداد الفرد' ودرجة الامتحان النهائي. وبالإضافة إلى ذلك، كان هناك ارتباط كبير بين نظام التعليم الثانوي ونتيجة 'اختبارات ضمان استعداد الفرد'، حيث لوحظ أفضل أداء بين الطلاب القادمين من المدارس التي تستخدم المنهج البريطاني.
الاستنتاجات: كان التصور العام وموقف الطلاب تجاه نظام 'التعلم المبني على فريق' إيجابيا وواعدا. ومع ذلك، فإن هناك بعض الملحوظات ومجالات للقلق يجب إعادة النظر فيها ومعالجتها لتحسين 'التعلم المبني على فريق' كأداة تعليمية.
Keywords: GRAT; IRAT; Medical education; PBL; TBL.
Figures
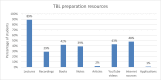

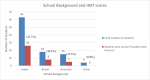
References
-
- Prince M. Does active learning work? A review of the research. J Eng Educ. 2004;93(3):223–231.
-
- Staun M., Bergstrom B., Wadensten B. Evaluation of a PBL strategy in clinical supervision of nursing students: patient-centred training in student-dedicated treatment rooms. Nurse Educ Today. 2010;30(7):631–637. - PubMed
-
- Nieboer E. A problem-based, self-directed approach to the teaching of the principles of environmental and human toxicology. J Environ Monit. 2002;4(1):14N–16N. - PubMed
-
- Faisal R. Problem-based learning in comparison with lecture-based learning among medical students. J Pakistan Med Assoc. 2016;66(6):650–653. - PubMed
-
- Fatmi M. The effectiveness of team-based learning on learning outcomes in health professions education: BEME Guide No. 30. Med Teach. 2013;35(12):e1608–e1624. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

