KMT2D deficiency enhances the anti-cancer activity of L48H37 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 31435462
- PMCID: PMC6700028
- DOI: 10.4251/wjgo.v11.i8.599
KMT2D deficiency enhances the anti-cancer activity of L48H37 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: Novel therapeutic strategies are urgently needed for patients with a delayed diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) in order to improve their chances of survival. Recent studies have shown potent anti-neoplastic effects of curcumin and its analogues. In addition, the role of histone methyltransferases on cancer therapeutics has also been elucidated. However, the relationship between these two factors in the treatment of pancreatic cancer remains unknown. Our working hypothesis was that L48H37, a novel curcumin analog, has better efficacy in pancreatic cancer cell growth inhibition in the absence of histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2D (KMT2D).
Aim: To determine the anti-cancer effects of L48H37 in PDAC, and the role of KMT2D on its therapeutic efficacy.
Methods: The viability and proliferation of primary (PANC-1 and MIA PaCa-2) and metastatic (SW1990 and ASPC-1) PDAC cell lines treated with L48H37 was determined by CCK8 and colony formation assay. Apoptosis, mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, and cell cycle profile were determined by staining the cells with Annexin-V/7-AAD, JC-1, DCFH-DA, and PI respectively, as well as flow cytometric acquisition. In vitro migration was assessed by the wound healing assay. The protein and mRNA levels of relevant factors were analyzed using Western blotting, immunofluorescence and real time-quantitative PCR. The in situ expression of KMT2D in both human PDAC and paired adjacent normal tissues was determined by immunohistochemistry. In vivo tumor xenografts were established by injecting nude mice with PDAC cells. Bioinformatics analyses were also conducted using gene expression databases and TCGA.
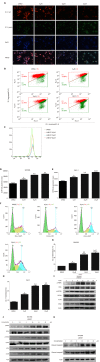
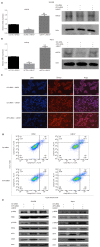
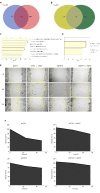
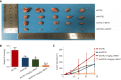
Results: L48H37 inhibited the proliferation and induced apoptosis in SW1990 and ASPC-1 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner, while also reducing MMP, increasing ROS levels, arresting cell cycle at the G2/M stages and activating the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-associated protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase/eukaryotic initiation factor 2α/activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4)/CHOP signaling pathway. Knocking down ATF4 significantly upregulated KMT2D in PDAC cells, and also decreased L48H37-induced apoptosis. Furthermore, silencing KMT2D in L48H37-treated cells significantly augmented apoptosis and the ER stress pathway, indicating that KMT2D depletion is essential for the anti-neoplastic effects of L48H37. Administering L48H37 to mice bearing tumors derived from control or KMT2D-knockdown PDAC cells significantly decreased the tumor burden. We also identified several differentially expressed genes in PDAC cell lines expressing very low levels of KMT2D that were functionally categorized into the extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway. The KMT2D high- and low-expressing PDAC patients from the TCGA database showed similar survival rates,but higher KMT2D expression was associated with poor tumor grade in clinical and pathological analyses.
Conclusion: L48H37 exerts a potent anti-cancer effect in PDAC, which is augmented by KMT2D deficiency.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Curcumin analog; Histone methyltransferase 2D; Pancreatic neoplasms; Therapeutic effects.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: There is no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Curcumin analog L48H37 induces apoptosis through ROS-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress and STAT3 pathways in human lung cancer cells.Mol Carcinog. 2017 Jul;56(7):1765-1777. doi: 10.1002/mc.22633. Epub 2017 Mar 10. Mol Carcinog. 2017. PMID: 28218464
-
Upregulation of KLK8 Predicts Poor Prognosis in Pancreatic Cancer.Front Oncol. 2021 Jul 30;11:624837. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.624837. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34395235 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin Analog L48H37 Induces Apoptosis in Human Oral Cancer Cells by Activating Caspase Cascades and Downregulating the Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins through JNK/p38 Signaling.Am J Chin Med. 2024;52(2):565-581. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X24500241. Epub 2024 Mar 14. Am J Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 38480502
-
Direct Endoplasmic Reticulum Targeting by the Selective Alkylphospholipid Analog and Antitumor Ether Lipid Edelfosine as a Therapeutic Approach in Pancreatic Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Aug 19;13(16):4173. doi: 10.3390/cancers13164173. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone-Lysine N-Methyltransferase 2D (KMT2D) Impending Therapeutic Target for the Management of Cancer: The Giant Rats Tail.J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2025;44(1):31-36. doi: 10.1615/JEnvironPatholToxicolOncol.2024053872. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39462447 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and Interaction Analysis of Molecular Markers in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma by Bioinformatics and Next-Generation Sequencing Data Analysis.Bioinform Biol Insights. 2023 Jul 25;17:11779322231186719. doi: 10.1177/11779322231186719. eCollection 2023. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2023. PMID: 37529485 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer-epigenetic function of the histone methyltransferase KMT2D and therapeutic opportunities for the treatment of KMT2D-deficient tumors.Oncotarget. 2021 Jun 22;12(13):1296-1308. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27988. eCollection 2021 Jun 22. Oncotarget. 2021. PMID: 34194626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High expression of KMT2D is a promising biomarker for poor gastric cancer prognosis.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Mar 15;15(3):1964-1972. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 37056814 Free PMC article.
-
CSTF2T facilitates pancreatic adenocarcinoma growth and metastasis by elevating H3K4Me1 methylation of CALB2 via ASH2L.Cancer Biol Ther. 2023 Dec 31;24(1):2216041. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2023.2216041. Cancer Biol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37287122 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin Analogue L48H37 Suppresses Human Osteosarcoma U2OS and MG-63 Cells' Migration and Invasion in Culture by Inhibition of uPA via the JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway.Molecules. 2020 Dec 23;26(1):30. doi: 10.3390/molecules26010030. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33374783 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Neoptolemos JP, Kleeff J, Michl P, Costello E, Greenhalf W, Palmer DH. Therapeutic developments in pancreatic cancer: current and future perspectives. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;15:333–348. - PubMed
-
- Papke DJ, Jr, Nowak JA, Yurgelun MB, Frieden A, Srivastava A, Lindeman NI, Sholl LM, MacConaill LE, Dong F. Validation of a targeted next-generation sequencing approach to detect mismatch repair deficiency in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Mod Pathol. 2018;31:1882–1890. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

