Structural connectivity profile supports laterality of the salience network
- PMID: 31436006
- PMCID: PMC6864895
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.24769
Structural connectivity profile supports laterality of the salience network
Abstract
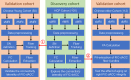
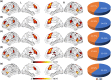
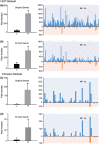
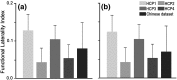
The salience network (SN) is mainly involved in detecting and filtering multimodal salient stimuli, and mediating the switch between the default mode network and central executive network. Early studies have indicated a right-sided dominance in the functional organization of the SN; however, the anatomical basis of the functional lateralization remains unclear. Here, we hypothesized that the structural connectivity profile between the frontoinsular cortex (FIC) and dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (dACC), which are two core hubs of the SN, is also dominant in the right hemisphere. Based on diffusion and resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (rfMRI) of adult healthy volunteers in independent datasets, we found a stable right-sided laterality of both the FIC-dACC structural and functional connectivity in both the human connectome project cohort and a local Chinese cohort. Furthermore, a significant effect of aging on the integrity of the right FIC-dACC structural connectivity was also identified. The right-sided laterality of the structural organization of the SN may help us to better understand the functional roles of the SN in the normal human brain.
Keywords: aging; diffusion magnetic resonance imaging; dorsal anterior cingulate cortex; frontal insula cortex; laterality; salience network; structural connectivity.
© 2019 The Authors. Human Brain Mapping published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




References
-
- Allman, J. M. , Tetreault, N. A. , Hakeem, A. Y. , Manaye, K. F. , Semendeferi, K. , Erwin, J. M. , … Hof, P. R. (2010). The von Economo neurons in frontoinsular and anterior cingulate cortex in great apes and humans. Brain Structure & Function, 214(5–6), 495–517. - PubMed
-
- Allman, J. M. , Watson, K. K. , Tetreault, N. A. , & Hakeem, A. Y. (2005). Intuition and autism: A possible role for Von Economo neurons. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 9(8), 367–373. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner, J. (2007). A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. NeuroImage, 38(1), 95–113. - PubMed
-
- Bargmann, C. I. , & Marder, E. (2013). From the connectome to brain function. Nature Methods, 10(6), 483–490. - PubMed
-
- Basser, P. J. , Pajevic, S. , Pierpaoli, C. , Duda, J. , & Aldroubi, A. (2000). In vivo fiber tractography using DT‐MRI data. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 44(4), 625–632. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2017M611175/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation/International
- 2017YFC0909201/National Key Research and Development Program of China/International
- 2018YFC1314300/National Key Research and Development Program of China/International
- 81425013/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 81571659/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

